Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases
- PMID: 35524448
- PMCID: PMC9637239
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.32562
Endoplasmic reticulum stress in liver diseases
Abstract
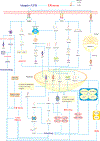
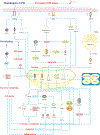
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is an intracellular organelle that fosters the correct folding of linear polypeptides and proteins, a process tightly governed by the ER-resident enzymes and chaperones. Failure to shape the proper 3-dimensional architecture of proteins culminates in the accumulation of misfolded or unfolded proteins within the ER, disturbs ER homeostasis, and leads to canonically defined ER stress. Recent studies have elucidated that cellular perturbations, such as lipotoxicity, can also lead to ER stress. In response to ER stress, the unfolded protein response (UPR) is activated to reestablish ER homeostasis ("adaptive UPR"), or, conversely, to provoke cell death when ER stress is overwhelmed and sustained ("maladaptive UPR"). It is well documented that ER stress contributes to the onset and progression of multiple hepatic pathologies including NAFLD, alcohol-associated liver disease, viral hepatitis, liver ischemia, drug toxicity, and liver cancers. Here, we review key studies dealing with the emerging role of ER stress and the UPR in the pathophysiology of liver diseases from cellular, murine, and human models. Specifically, we will summarize current available knowledge on pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions that may be used to target maladaptive UPR for the treatment of nonmalignant liver diseases.
Copyright © 2023 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
GK holds research contracts with Daiichi Sankyo, Eleor, Kaleido, Lytix Pharma, PharmaMar, Samsara, Sanofi, Sotio, Vascage and Vasculox/Tioma. GK is on the Board of Directors of the Bristol Myers Squibb Foundation France. GK is a scientific co-founder of everImmune, Samsara Therapeutics and Therafast Bio. GK is the inventor of patents covering therapeutic targeting of aging, cancer, cystic fibrosis and metabolic disorders.
Figures

References
-
- Wang M, Kaufman RJ. Protein misfolding in the endoplasmic reticulum as a conduit to human disease. Nature 2016;529:326–335. - PubMed
-
- Ajoolabady A, Wang S, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, Uversky VN, Sowers JR, Aslkhodapasandhokmabad H, et al. ER stress in cardiometabolic diseases: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutics. Endocrine Reviews 2021. - PubMed
-
- Ren J, Bi Y, Sowers JR, Hetz C, Zhang Y. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in cardiovascular diseases. Nature Reviews Cardiology 2021;18:499–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

