Dioscin ameliorates inflammatory bowel disease by up-regulating miR-125a-5p to regulate macrophage polarization
- PMID: 35524480
- PMCID: PMC9169194
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.24455
Dioscin ameliorates inflammatory bowel disease by up-regulating miR-125a-5p to regulate macrophage polarization
Abstract
Purpose: Dioscin has been proven to have anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory, and anti-infection roles. However, the role of Dioscin in inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and its related mechanisms is unclear and needs further study.
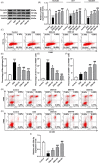
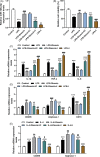
Methods: The colitis model in mice was established. After Dioscin (20, 40, or 80 mg/kg) treatment, the colon length was measured by a ruler. Histopathology, inflammatory cytokines, gut permeability, tight junction proteins, macrophage infiltration, macrophage polarization, and miR-125a-5p level were detected by hematoxylin-eosin staining, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR), FITC-dextran, Western blot, and flow cytometry. In vitro experiments, after RAW264.7 cells induced by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)/interleukin-4 (IL-4), were treated with Dioscin and miR-125a-5p inhibitor, miR-125a-5p level, cell vitality, inflammatory cytokines, and M1/M2 marker genes were measured by qRT-PCR and MTT assay.
Results: Dioscin (20, 40, or 80 mg/kg) relieved DSS-triggered colitis and restrained the serum and colon of pro-inflammatory cytokines expression. Meanwhile, different concentrations' Dioscin weakened M1 macrophage polarization but facilitated tight junction protein expressions, M2 macrophage polarization, and miR-125a-5p level in colitic mice. Moreover, miR-125a-5p inhibitor reversed the modulation of Dioscin on miR-125a-5p expression, cell vitality, and inflammatory cytokines in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced RAW264.7 cells. We further discovered that Dioscin restrained M1 marker gene (CD16) expression while intensifying M2 marker genes (CD206 and Arginase-1) expressions in vitro, which was reversed by miR-125a-5p inhibitor.
Conclusion: Dioscin modulated macrophage polarization by increasing miR-125a-5p, thereby improving the intestinal epithelial barrier function and reducing IBD.
Keywords: dextran sulfate sodium; dioscin; inflammatory bowel disease; lipopolysaccharide; miR-125a-5p.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Downregulation of lncRNA NEAT1 Ameliorates LPS-Induced Inflammatory Responses by Promoting Macrophage M2 Polarization via miR-125a-5p/TRAF6/TAK1 Axis.Inflammation. 2020 Aug;43(4):1548-1560. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01231-y. Inflammation. 2020. PMID: 32388658
-
Dioscin ameliorates murine ulcerative colitis by regulating macrophage polarization.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Oct;172:105796. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105796. Epub 2021 Jul 31. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34343656
-
The pentacyclic triterpene Lupeol switches M1 macrophages to M2 and ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Jan;30:74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.11.031. Epub 2015 Dec 3. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26655877
-
MiRNA-Mediated Macrophage Polarization and its Potential Role in the Regulation of Inflammatory Response.Shock. 2016 Aug;46(2):122-31. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000000604. Shock. 2016. PMID: 26954942 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Macrophage polarization in inflammatory bowel disease.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Dec 21;21(1):367. doi: 10.1186/s12964-023-01386-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 38129886 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A potential therapeutic approach for ulcerative colitis: targeted regulation of macrophage polarization through phytochemicals.Front Immunol. 2023 May 1;14:1155077. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1155077. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37197668 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Future Avenue of Treatment Ulcerative Colitis Targeting Macrophage Polarization: A Phytochemical Application.Crohns Colitis 360. 2024 Nov 28;6(4):otae070. doi: 10.1093/crocol/otae070. eCollection 2024 Oct. Crohns Colitis 360. 2024. PMID: 39668979 Free PMC article.
-
The potential role of miRNA in regulating macrophage polarization.Heliyon. 2023 Oct 31;9(11):e21615. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e21615. eCollection 2023 Nov. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 38027572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MiRNAs: a new target for Chinese medicine to repair the intestinal barrier in the treatment of ulcerative colitis.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1446554. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1446554. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39185319 Free PMC article.
-
Ginsenoside Rh2 suppresses ferroptosis in ulcerative colitis by targeting specific protein 1 by upregulating microRNA-125a-5p.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Sep 2;29(1):450. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02025-w. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39223620 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Head KA, Jurenka JS. Inflammatory bowel disease Part 1: ulcerative colitis–pathophysiology and conventional and alternative treatment options. Altern Med Rev. 2003;8(3):247‐283. - PubMed
-
- Hwang C, Ross V, Mahadevan U. Micronutrient deficiencies in inflammatory bowel disease: from A to zinc. Inflamm Bowel Dis. 2012;18(10):1961‐1981. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

