A programmable pAgo nuclease with RNA target preference from the psychrotolerant bacterium Mucilaginibacter paludis
- PMID: 35524569
- PMCID: PMC9122594
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkac315
A programmable pAgo nuclease with RNA target preference from the psychrotolerant bacterium Mucilaginibacter paludis
Abstract
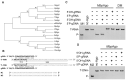
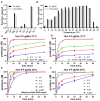
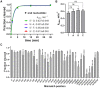
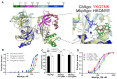
Argonaute (Ago) proteins are programmable nucleases found in eukaryotes and prokaryotes. Prokaryotic Agos (pAgos) share a high degree of structural homology with eukaryotic Agos (eAgos), and eAgos originate from pAgos. Although eAgos exclusively cleave RNA targets, most characterized pAgos cleave DNA targets. This study characterized a novel pAgo, MbpAgo, from the psychrotolerant bacterium Mucilaginibacter paludis which prefers to cleave RNA targets rather than DNA targets. Compared to previously studied Agos, MbpAgo can utilize both 5'phosphorylated(5'P) and 5'hydroxylated(5'OH) DNA guides (gDNAs) to efficiently cleave RNA targets at the canonical cleavage site if the guide is between 15 and 17 nt long. Furthermore, MbpAgo is active at a wide range of temperatures (4-65°C) and displays no obvious preference for the 5'-nucleotide of a guide. Single-nucleotide and most dinucleotide mismatches have no or little effects on cleavage efficiency, except for dinucleotide mismatches at positions 11-13 that dramatically reduce target cleavage. MbpAgo can efficiently cleave highly structured RNA targets using both 5'P and 5'OH gDNAs in the presence of Mg2+ or Mn2+. The biochemical characterization of MbpAgo paves the way for its use in RNA manipulations such as nucleic acid detection and clearance of RNA viruses.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Swarts D.C., Jore M.M., Westra E.R., Zhu Y., Janssen J.H., Snijders A.P., Wang Y., Patel D.J., Berenguer J., Brouns S.J.J.J.et al.. DNA-guided DNA interference by a prokaryotic Argonaute. Nature. 2014; 507:258–261. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

