Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Measures of First-phase Insulin Response and Their Predictive Ability for Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 35524749
- PMCID: PMC9282258
- DOI: 10.1210/clinem/dgac285
Oral Glucose Tolerance Test Measures of First-phase Insulin Response and Their Predictive Ability for Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Context: Decreased first-phase insulin response (FPIR) during intravenous glucose tolerance testing (IVGTT) is an early indicator of β-cell dysfunction and predictor of type 1 diabetes (T1D).
Objective: Assess whether oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) measures could serve as FPIR alternatives in their ability to predict T1D in autoantibody positive (Aab+) subjects.
Design: OGTT and IVGTT were performed within 30 days of each other. Eleven OGTT variables were evaluated for (1) correlation with FPIR and (2) T1D prediction.
Setting: Type 1 Diabetes TrialNet "Oral Insulin for Prevention of Diabetes in Relatives at Risk for T1D" (TN-07) and Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Diabetes (DPT-1) studies clinical sites.
Patients: TN-07 (n = 292; age 9.4 ± 6.1 years) and DPT-1 (n = 194; age 15.1 ± 10.0 years) Aab + relatives of T1D individuals.
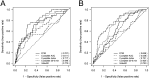
Main outcome measures: (1) Correlation coefficients of OGTT measures with FPIR and (2) T1D prediction at 2 years using area under receiver operating characteristic (ROCAUC) curves.
Results: Index60 showed the strongest correlation in DPT-1 (r = -0.562) but was weaker in TN-07 (r = -0.378). C-peptide index consistently showed good correlation with FPIR across studies (TN-07, r = 0.583; DPT-1, r = 0.544; P < 0.0001). Index60 and C-peptide index had the highest ROCAUCs for T1D prediction (0.778 vs 0.717 in TN-07 and 0.763 vs 0.721 in DPT-1, respectively; P = NS), followed by FPIR (0.707 in TN-07; 0.628 in DPT-1).
Conclusions: C-peptide index was the strongest measure to correlate with FPIR in both studies. Index60 and C-peptide index had the highest predictive accuracy for T1D and were comparable. OGTTs could be considered instead of IVGTTs for subject stratification in T1D prevention trials.
Keywords: C-peptide index; Index60; TrialNet; first-phase insulin response; oral glucose tolerance test; type 1 diabetes.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
References
-
- Del Prato S, Tiengo A. The importance of first-phase insulin secretion: implications for the therapy of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2001;17(3):164-174. - PubMed
-
- Sosenko JM, Skyler JS, Beam CA, et al. ; Type 1 Diabetes T, Diabetes Prevention Trial-Type 1 Study G. Acceleration of the loss of the first-phase insulin response during the progression to type 1 diabetes in diabetes prevention trial-type 1 participants. Diabetes. 2013;62(12):4179-4183. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vardi P, Crisa L, Jackson RA. Predictive value of intravenous glucose tolerance test insulin secretion less than or greater than the first percentile in islet cell antibody positive relatives of type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetic patients. Diabetologia. 1991;34(2):93-102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 DK085476/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061010/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085453/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103282/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK106993/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061042/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085509/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UC4 DK117009/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases
- U01 DK085466/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103153/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061058/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106984/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085499/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107013/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103266/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK107014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK106994/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK061034/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085461/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK103180/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085465/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DK085504/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

