Early Changes in Puffing Intensity When Exclusively Using Open-Label Very Low Nicotine Content Cigarettes
- PMID: 35524988
- PMCID: PMC9597006
- DOI: 10.1093/ntr/ntac118
Early Changes in Puffing Intensity When Exclusively Using Open-Label Very Low Nicotine Content Cigarettes
Abstract
Introduction: In response to reducing cigarette nicotine content, people who smoke could attempt to compensate by using more cigarettes or by puffing on individual cigarettes with greater intensity. Such behaviors may be especially likely under conditions where normal nicotine content (NNC) cigarettes are not readily accessible. The current within-subject, residential study investigated whether puffing intensity increased with very low nicotine content (VLNC) cigarette use, relative to NNC cigarette use, when no other nicotine products were available.
Aims and methods: Sixteen adults who smoke daily completed two four-night hotel stays in Charleston, South Carolina (United States) in 2018 during which only NNC or only VLNC cigarettes were accessible. We collected the filters from all smoked cigarettes and measured the deposited solanesol to estimate mouth-level nicotine delivery per cigarette. These estimates were averaged within and across participants, per each 24-h period. We then compared the ratio of participant-smoked VLNC and NNC cigarette mouth-level nicotine with the ratio yielded by cigarette smoking machines (when puffing intensity is constant).
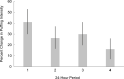
Results: Average mouth-level nicotine estimates from cigarettes smoked during the hotel stays indicate participants puffed VLNC cigarettes with greater intensity than NNC cigarettes in each respective 24-h period. However, this effect diminished over time (p < .001). Specifically, VLNC puffing intensity was 40.0% (95% CI: 29.9, 53.0) greater than NNC puffing intensity in the first period, and 16.1% (95% CI: 6.9, 26.0) greater in the fourth period.
Conclusion: Average puffing intensity per cigarette was elevated with exclusive VLNC cigarette use, but the extent of this effect declined across four days.
Implications: In an environment where no other sources of nicotine are available, people who smoke daily may initially attempt to compensate for cigarette nicotine reduction by puffing on individual cigarettes with greater intensity. Ultimately, the compensatory behavior changes required to achieve usual nicotine intake from VLNC cigarettes are drastic and unrealistic. Accordingly, people are unlikely to sustain attempts to compensate for very low cigarette nicotine content.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Impact of Reducing Nicotine Content on Adolescent Cigarette Smoking and Nicotine Exposure: Results From a Randomized Controlled Trial.Nicotine Tob Res. 2023 Apr 6;25(5):918-927. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntac279. Nicotine Tob Res. 2023. PMID: 36482794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Smoking Topography Characteristics of Very Low Nicotine Content Cigarettes, With and Without Nicotine Replacement, in Smokers With Schizophrenia and Controls.Nicotine Tob Res. 2016 Sep;18(9):1807-12. doi: 10.1093/ntr/ntw089. Epub 2016 Mar 19. Nicotine Tob Res. 2016. PMID: 26995794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reactions to reduced nicotine content cigarettes in a sample of young adult, low-frequency smokers.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021 Sep;238(9):2429-2438. doi: 10.1007/s00213-021-05864-1. Epub 2021 May 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2021. PMID: 33982143 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of menthol on nicotine reduction: Pooled results from two double-blind randomized controlled trials.Brain Res Bull. 2022 Oct 15;189:131-138. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2022.08.019. Epub 2022 Aug 28. Brain Res Bull. 2022. PMID: 36038015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of very low nicotine content cigarettes on smoking across vulnerable populations.Prev Med. 2022 Dec;165(Pt B):107099. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2022.107099. Epub 2022 May 26. Prev Med. 2022. PMID: 35642796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Darby TD, McNamee JE, van Rossum JM.. Cigarette smoking pharmacokinetics and its relationship to smoking behaviour. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1984;9(5):435–49. - PubMed
-
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Advance notice of proposed rulemaking: tobacco product standard for nicotine level of combusted cigarettes. Document number: 2018–05345. Fed Regist 2018:1–99.
-
- Strasser AA, Lerman C, Sanborn PM, Pickworth WB, Feldman EA.. New lower nicotine cigarettes can produce compensatory smoking and increased carbon monoxide exposure. Drug Alcohol Depend. 2007;86(2-3):294–300. - PubMed

