Nitric oxide biosensor uncovers diminished ferrous iron-dependency of cultured cells adapted to physiological oxygen levels
- PMID: 35525027
- PMCID: PMC9079701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102319
Nitric oxide biosensor uncovers diminished ferrous iron-dependency of cultured cells adapted to physiological oxygen levels
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Nitric oxide biosensor uncovers diminished ferrous iron-dependency of cultured cells adapted to physiological oxygen levels" [Redox Biol. 53 (2022) 102319].Redox Biol. 2022 Aug;54:102364. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2022.102364. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Redox Biol. 2022. PMID: 35697638 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
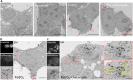
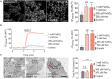
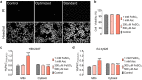
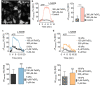
Iron is an essential metal for cellular metabolism and signaling, but it has adverse effects in excess. The physiological consequences of iron deficiency are well established, yet the relationship between iron supplementation and pericellular oxygen levels in cultured cells and their downstream effects on metalloproteins has been less explored. This study exploits the metalloprotein geNOps in cultured HEK293T epithelial and EA.hy926 endothelial cells to test the iron-dependency in cells adapted to standard room air (18 kPa O2) or physiological normoxia (5 kPa O2). We show that cells in culture require iron supplementation to activate the metalloprotein geNOps and demonstrate for the first time that cells adapted to physiological normoxia require significantly lower iron compared to cells adapted to hyperoxia. This study establishes an essential role for recapitulating oxygen levels in vivo and uncovers a previously unrecognized requirement for ferrous iron supplementation under standard cell culture conditions to achieve geNOps functionality.
Keywords: Cell culture; Culture media; Ferric iron; Ferrous iron; Hydrogen peroxide; Hyperoxia; NO bioavailability; Normoxia; Pericellular oxygen; geNOps.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Rouault T.A. Iron metabolism in the CNS: implications for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2013;14:551–564. - PubMed
-
- Beard J.L. Iron biology in immune function, muscle metabolism and neuronal functioning. J. Nutr. 2001;131:568S–580S. - PubMed
-
- Stephenson E., Nathoo N., Mahjoub Y., Dunn J.F., Yong V.W. Iron in multiple sclerosis: roles in neurodegeneration and repair. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014;10:459–468. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

