Target-triggered cascade signal amplification for sensitive electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 with clinical application
- PMID: 35525596
- PMCID: PMC9020774
- DOI: 10.1016/j.aca.2022.339846
Target-triggered cascade signal amplification for sensitive electrochemical detection of SARS-CoV-2 with clinical application
Abstract
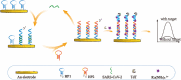
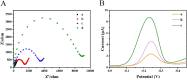
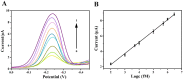
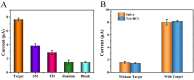
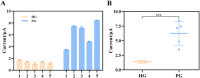
The spread of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has led to the outbreak of the 2019 coronavirus (COVID-19) disease, which greatly challenges the global economy and health. Simple and sensitive diagnosis of COVID-19 at the early stage is important to prevent the spread of pandemics. Herein, we have proposed a target-triggered cascade signal amplification in this work for sensitive analysis of SARS-CoV-2 RNA. Specifically, the presence of SARS-CoV-2 RNA can trigger the catalytic hairpin assembly to generate plenty of DNA duplexes with free 3'-OH termini, which can be recognized and catalyzed by the terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) to generate long strand DNA. The prolonged DNA can absorb substantial Ru(NH3)63+ molecules via electrostatic interaction and produce an enhanced current response. The incorporation of catalytic hairpin assembly and TdT-mediated polymerization effectively lowers the detection limit to 45 fM, with a wide linear range from 0.1 pM to 3000 pM. Moreover, the proposed strategy possesses excellent selectivity to distinguish target RNA with single-base mismatched, three-base mismatched, and random sequences. Notably, the proposed electrochemical biosensor can be applied to analyze targets in complex circumstances containing 10% saliva, which implies its high stability and anti-interference. Moreover, the proposed strategy has been successfully applied to SARS CoV-2 RNA detection in clinical samples and may have the potential to be cultivated as an effective tool for COVID-19 diagnosis.
Keywords: COVID-19; Cascade signal amplification; Electrochemical biosensor; SARS-CoV-2 RNA.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
-
- Shi L., Wang L., Ma X., Fang X., Xiang L., Yi Y., Li J., Luo Z., Li G. Aptamer-functionalized nanochannels for one-step detection of SARS-CoV-2 in samples from COVID-19 patients. Anal. Chem. 2021;93(49):16646–16654. - PubMed
-
- Feng W., Newbigging A.M., Le C., Pang B., Peng H., Cao Y., Wu J., Abbas G., Song J., Wang D.-B., Cui M., Tao J., Tyrrell D.L., Zhang X.-E., Zhang H., Le X.C. Molecular diagnosis of COVID-19: challenges and research needs. Anal. Chem. 2020;92(15):10196–10209. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

