Association between microRNAs 10b/21/34a and acute toxicity in glioblastoma patients treated with radiotherapy and temozolomide
- PMID: 35525840
- PMCID: PMC9079078
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-11445-9
Association between microRNAs 10b/21/34a and acute toxicity in glioblastoma patients treated with radiotherapy and temozolomide
Abstract
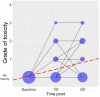
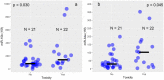
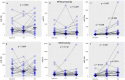
A personalized approach to chemoradiation is important in reducing its potential side effects and identifying a group of patients prone to toxicity. MicroRNAs have been shown to have a predictive potential for radiotoxicity. The goal of the study was to test if levels of miRNA in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of glioblastoma patients are associated with toxicity and to identify the peak time point for toxicity. MicroRNA-10b/21/34a levels were measured in 43 patients with and without toxicity, at baseline, at the 15th, and at the 30th fraction by Real-Time quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction. MicroRNA-10b/21 levels increased with toxicity grade (p = 0.014; p = 0.013); miR-21/34a levels were significantly different between patients with and without toxicity at the 15th fraction (p = 0.030; p = 0.045), while miR-34a levels significantly changed during treatment (p < 0.001). All three miRNAs showed a significantly high positive correlation with one another. MiR-34a might be considered as a predictive factor for toxicity due to its changes during treatment, and differences between the groups with and without toxicity; miR-10b might be used to predict toxicity; miR-10b/21 might be used for predicting the grade of toxicity in GB patients.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Peponi E, et al. Prognostic factors in glioblastoma patients managed with radiotherapy combined with temozolomide. J. BUON. 2014;19:718–723. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

