Two adjacent phosphorylation sites in the C-terminus of the channel's α-subunit have opposing effects on epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity
- PMID: 35525869
- PMCID: PMC9192390
- DOI: 10.1007/s00424-022-02693-9
Two adjacent phosphorylation sites in the C-terminus of the channel's α-subunit have opposing effects on epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Two adjacent phosphorylation sites in the C-terminus of the channel's α-subunit have opposing effects on epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) activity.Pflugers Arch. 2022 Sep;474(9):1037. doi: 10.1007/s00424-022-02717-4. Pflugers Arch. 2022. PMID: 35676334 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
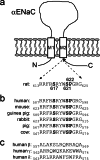
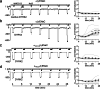
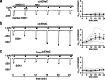
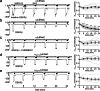
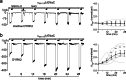
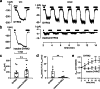
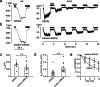
How phosphorylation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) contributes to its regulation is incompletely understood. Previously, we demonstrated that in outside-out patches ENaC activation by serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase isoform 1 (SGK1) was abolished by mutating a serine residue in a putative SGK1 consensus motif RXRXX(S/T) in the channel's α-subunit (S621 in rat). Interestingly, this serine residue is followed by a highly conserved proline residue rather than by a hydrophobic amino acid thought to be required for a functional SGK1 consensus motif according to in vitro data. This suggests that this serine residue is a potential phosphorylation site for the dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylated and regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2), a prototypical proline-directed kinase. Its phosphorylation may prime a highly conserved preceding serine residue (S617 in rat) to be phosphorylated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 β (GSK3β). Therefore, we investigated the effect of DYRK2 on ENaC activity in outside-out patches of Xenopus laevis oocytes heterologously expressing rat ENaC. DYRK2 included in the pipette solution significantly increased ENaC activity. In contrast, GSK3β had an inhibitory effect. Replacing S621 in αENaC with alanine (S621A) abolished the effects of both kinases. A S617A mutation reduced the inhibitory effect of GKS3β but did not prevent ENaC activation by DYRK2. Our findings suggest that phosphorylation of S621 activates ENaC and primes S617 for subsequent phosphorylation by GSK3β resulting in channel inhibition. In proof-of-concept experiments, we demonstrated that DYRK2 can also stimulate ENaC currents in microdissected mouse distal nephron, whereas GSK3β inhibits the currents.
Keywords: Dual-specificity tyrosine phosphorylated and regulated kinase 2 (DYRK2); Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC); Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta (GSK3β); Microdissected mouse distal nephron; Patch clamp; Serum- and glucocorticoid-induced kinase isoform 1 (SGK1); Xenopus laevis oocytes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

