The relationship between previous pulmonary tuberculosis and risk of lung cancer in the future
- PMID: 35525982
- PMCID: PMC9078090
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-022-00434-2
The relationship between previous pulmonary tuberculosis and risk of lung cancer in the future
Abstract
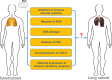
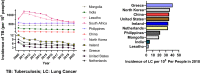
Various investigations have expanded the views that tuberculosis is an important risk factor for lung cancer occurrence. Lung cancer originates from chronic inflammation and infection. It is becoming clearer that Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) in tuberculosis patients meticulously schemes multiple mechanisms to induce tumor formation and is indispensable to participate in the occurrence of lung cancer. In addition, some additional factors such as age, sex and smoking, accelerate the development of lung cancer after Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. The clarification of these insights is fostering new diagnoses and therapeutic approaches to prevention of the patients developing from tuberculosis into lung cancer.
Keywords: COX-2; CRP; Cytokine; DNA damage; Lung cancer; ROS; Risk factor; Tuberculosis.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Bae S, Kim YJ, Kim MJ, Kim JH, Yun SC, Jung J, Kim MJ, Chong YP, Kim SH, Choi SH, et al. Risk of tuberculosis in patients with cancer treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors: a nationwide observational study. J Immunother Cancer. 2021;9(9):e002960. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2021-002960. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

