Multifunctional thermo-sensitive hydrogel for modulating the microenvironment in Osteoarthritis by polarizing macrophages and scavenging RONS
- PMID: 35526013
- PMCID: PMC9077879
- DOI: 10.1186/s12951-022-01422-9
Multifunctional thermo-sensitive hydrogel for modulating the microenvironment in Osteoarthritis by polarizing macrophages and scavenging RONS
Abstract
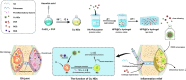
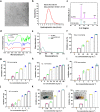
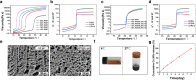
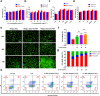
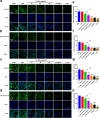
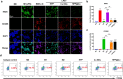
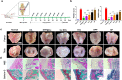
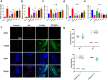
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common degenerative joint disease that can lead to disability. Blocking the complex malignant feedback loop system dominated by oxidative stress and pro-inflammatory factors is the key to treating OA. Here, we develop a multifunctional composite thermo-sensitive hydrogel (HPP@Cu gel), which is utilized by Poloxamer 407 (P407) and hyaluronic acid (HA) mixture as the gel matrix, then physically mixed with copper nanodots (Cu NDs) and platelet-rich plasma (PRP). Cu NDs is a novel nano-scavenger of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (RONS) with efficient free radical scavenging activity. HPP@Cu gel is injected into the articular cavity, where it form an in situ gel that slowly released Cu NDs, HA, and PRP, prolonging the duration of drug action. Our results indicate that HPP@Cu gel could efficiently remove RONS from inflammatory sites and promote repolarization of macrophages to an anti-inflammatory phenotype. The HPP@Cu gel therapy dramatically reduces cartilage degradation and inflammatory factor production in OA rats. This study provides a reliable reference for the application of injectable hydrogels in inflammatory diseases associated with oxidative stress.
Keywords: Copper nanodots; Macrophage polarization; Osteoarthritis; Reactive oxygen and nitrogen species; Thermo-sensitive hydrogels.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hyaluronic acid composite hydrogel with enhanced lubrication and controllable drug release for the mitigation of osteoarthritis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2025 May;308(Pt 3):142677. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2025.142677. Epub 2025 Mar 29. Int J Biol Macromol. 2025. PMID: 40164244
-
Nanozyme-enhanced injectable hyaluronic acid-based hydrogel for the treatment of osteoarthritis.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Dec;282(Pt 2):136819. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.136819. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 39447781
-
Dual-Functional Injectable Hydrogel for Osteoarthritis Treatments.Adv Healthc Mater. 2024 Feb;13(5):e2302551. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202302551. Epub 2023 Nov 30. Adv Healthc Mater. 2024. PMID: 37988224
-
Mechanisms of Action and Efficacy of Hyaluronic Acid, Corticosteroids and Platelet-Rich Plasma in the Treatment of Temporomandibular Joint Osteoarthritis-A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 9;22(14):7405. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147405. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299024 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Hyaluronic Acid for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Am J Sports Med. 2021 Jan;49(1):249-260. doi: 10.1177/0363546520909397. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Am J Sports Med. 2021. PMID: 32302218
Cited by
-
Thermosensitive In Situ Gels for Joint Disorders: Pharmaceutical Considerations in Intra-Articular Delivery.Gels. 2022 Nov 8;8(11):723. doi: 10.3390/gels8110723. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36354630 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-regulating strategy against rheumatoid arthritis by inducing tolerogenic dendritic cells with modified zinc peroxide nanoparticles.J Nanobiotechnology. 2022 Jul 14;20(1):323. doi: 10.1186/s12951-022-01536-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2022. PMID: 35836178 Free PMC article.
-
Carnosine, Zinc and Copper: A Menage a Trois in Bone and Cartilage Protection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 11;24(22):16209. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216209. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38003398 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of chondrocyte cell death in osteoarthritis: implications for disease progression and treatment.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Sep 9;19(1):550. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-05055-6. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39252111 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanocomposite Hydrogels: A Promising Approach for the Treatment of Degenerative Joint Diseases.Small Sci. 2024 Sep 3;4(11):2400236. doi: 10.1002/smsc.202400236. eCollection 2024 Nov. Small Sci. 2024. PMID: 40213463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, AlMazroa MA, Memish ZA. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010 (vol 380, pg 2095, 2012) Lancet. 2013;381:628–628. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60704-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Silverstein FE, Faich G, Goldstein JL, Simon LS, Pincus T, Whelton A, Makuch R, Eisen G, Agrawal NM, Stenson WF, et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: the CLASS study: a randomized controlled trial. Celecoxib Long-term Arthritis Safety Study. JAMA. 2000;284:1247–1255. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.10.1247. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

