Intrarenal arterial administration of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively preserved the residual renal function of diabetic kidney disease in rat
- PMID: 35526048
- PMCID: PMC9080206
- DOI: 10.1186/s13287-022-02857-5
Intrarenal arterial administration of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells effectively preserved the residual renal function of diabetic kidney disease in rat
Abstract
Background: This experimental study was designed as a preclinical study for testing the hypothesis that intrarenal arterial (IRA) transfusion of human umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (HUCDMSCs) therapy preserved the residual renal function of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in rat [induction by 5/6 nephrectomy of left kidney and right nephrectomy, followed by intraperitoneal administration of aminoguanidine (180 mg/kg) and streptozotocin (30 mg/kg)].
Methods: Animals (n = 24) were categorized into group 1 (sham-operated control), group 2 (DKD), group 3 [DKD + HUCDMSCs (2.1 × 105/IRA injection at day 28 after CKD induction)] and group 4 [(DKD + HUCDMSCs (6.3 × 105/IRA injection)].
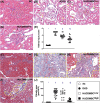
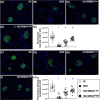
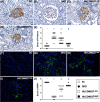
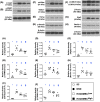
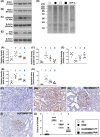
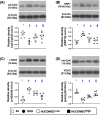
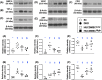
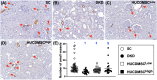
Results: By day 60 after DKD induction, the kidneys were harvested and the result showed that the creatinine level, ratio of urine protein/urine creatinine and kidney injury score were lowest in group 1, highest in group 2 and significantly lower in group 4 than in group 3 (all p < 0.0001). The protein expressions of apoptotic (cleaved caspase-3/cleaved PARP/mitochondrial Bax), fibrotic (TGF-ß/p-Smad3), autophagic (ratio of LC3B-II/LC3B-I, Atg5/Beclin-1), oxidative stress (NOX-1/NOX-2/oxidized protein/p22phox), mitochondrial/DNA-damaged (cytosolic-cytochrome-C/DRP1/γ-H2AX) and inflammatory (MMP-9/TNF-α/p-NF-κB) biomarkers exhibited an identical pattern, whereas the protein expressions of angiogenesis factors (CD31/vWF/vascularity) exhibited an opposite pattern of creatinine level among the groups (all p < 0.0001). Histopathological findings demonstrated the renal tubular-damaged (KIM-1)/kidney fibrosis area/oxidative stress (8-OHdG + cells) expressed an identical pattern, whereas the podocyte components (ZO-1/synaptopodin/podocin) exhibited an opposite pattern of creatinine level among the groups (all p < 0.0001). No tumorigenesis or immune rejection event was identified.
Conclusion: IRA injection of xenogeneic MSCs was safe and effectively protected the residual renal function and architectural integrity in DKD rat.
Keywords: Diabetic CKD; Renal function; Xenogeneic mesenchymal stem cell.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read the journal’s policy on disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and the journal’s authorship agreement. The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. The article has been reviewed and approved by all named authors.
Figures

References
-
- Aranson NJ, Lancaster RT, Ergul EA, Conrad MF, LaMuraglia GM, Kwolek CJ, Cambria RP, Patel VI. Chronic kidney disease class predicts mortality after abdominal aortic aneurysm repair in propensity-matched cohorts from the medicare population. Ann Surg. 2016;264:386–391. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000001519. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Metra M, Nodari S, Parrinello G, Bordonali T, Bugatti S, Danesi R, Fontanella B, Lombardi C, Milani P, Verzura G, Cotter G, Dittrich H, Massie BM, Dei Cas L. Worsening renal function in patients hospitalised for acute heart failure: clinical implications and prognostic significance. Eur J Heart Fail. 2008;10:188–195. doi: 10.1016/j.ejheart.2008.01.011. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cowie MR, Komajda M, Murray-Thomas T, Underwood J, Ticho B, Investigators P. Prevalence and impact of worsening renal function in patients hospitalized with decompensated heart failure: results of the prospective outcomes study in heart failure (POSH) Eur Heart J. 2006;27:1216–1222. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehi859. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

