Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in MS patients on disease modifying therapies during the Delta and the Omicron waves in Italy
- PMID: 35526306
- PMCID: PMC9069178
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2022.104042
Breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections after COVID-19 mRNA vaccination in MS patients on disease modifying therapies during the Delta and the Omicron waves in Italy
Abstract
Background: In this study we aimed to monitor the risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infection in patients with MS (pwMS) under different DMTs and to identify correlates of reduced protection.
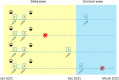
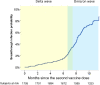
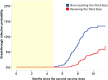
Methods: This is a prospective Italian multicenter cohort study, long-term clinical follow-up of the CovaXiMS (Covid-19 vaccine in Multiple Sclerosis) study. 1855 pwMS scheduled for SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination were enrolled and followed up to a mean time of 10 months. The cumulative incidence of breakthrough Covid-19 cases in pwMS was calculated before and after December 2021, to separate the Delta from the Omicron waves and to account for the advent of the third vaccine dose.
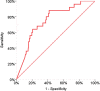
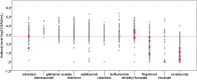
Findings: 1705 pwMS received 2 m-RNA vaccine doses, 21/28 days apart. Of them, 1508 (88.5%) had blood assessment 4 weeks after the second vaccine dose and 1154/1266 (92%) received the third dose after a mean interval of 210 days (range 90-342 days) after the second dose. During follow-up, 131 breakthrough Covid-19 infections (33 during the Delta and 98 during the Omicron wave) were observed. The probability to be infected during the Delta wave was associated with SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels measured after 4 weeks from the second vaccine dose (HR=0.57, p < 0.001); the protective role of antibodies was preserved over the whole follow up (HR=0.57, 95%CI=0.43-0.75, p < 0.001), with a significant reduction (HR=1.40, 95%CI=1.01-1.94, p=0.04) for the Omicron cases. The third dose significantly reduced the risk of infection (HR=0.44, 95%CI=0.21-0.90,p=0.025) during the Omicron wave.
Interpretation: The risk of breakthrough SARS-CoV-2 infections is mainly associated with reduced levels of the virus-specific humoral immune response.
Funding: Supported by FISM - Fondazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla - cod. 2021/Special-Multi/001 and financed or co-financed with the '5 per mille' public funding.
Keywords: Breakthrough infections; COVID-19; Disease Modifying Treatments; Multiple Sclerosis.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Sormani MP received consulting fees from Roche, Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Sanofi, Celgene, Immunic, Geneuro, GSK, Medday; received payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Roche, Biogen Merck, Novartis, Sanofi, Celgene; participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Roche, Sanofi, Novartis, Merck. Uccelli A received grants (to his Institution) from FISM, Biogen, Roche, Alexion, Merck Serono; participated on a Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board (to his Institution) for BD, Biogen, Iqvia, Sanofi, Roche, Alexion, Bristol Myers Squibb. Ulivelli M received consulting fees from Biogen, Novartis, Serono. Caleri F received honoraria for lectures or presentation from Biogen, Merck, Teva, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, Roche; received support for attending meeting and travel grant from Biogen, Merck, Teva, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, Roche; received honoraria for participation on Advisory Boards from Biogen, Merck, Teva, Novartis, Sanofi-Genzyme, Roche. Cordioli C received grants or contracts from Roche, Novartis, Merck Serono, Biogen, Celgene; received consulting fees from Biogen. Inglese M received grants or contracts from FISM, INAIL, European Union. Laroni A received grants or contracts from Italian Ministry of University, Ministry of Health; received consulting fees from Merck, Biogen, Roche, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EEIG; received honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Mercks, Biogen, Roche, Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb Pharma EEIG. Salvetti M received grants or contracts from Biogen, Merck, Novartis; received payments or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Biogen, Merck, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi. Landi D received consulting fees from Merck Serono, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Roche, Novartis, TEVA; received payments or honoraria for lectures, presentations, speakers’ bureaus, manuscript writing or educational events from Merck Serono, Celgene, Bristol Myers Squibb, Biogen, Roche, Novartis, Sanofi Genzyme, Mylan; received support for attending meetings and/or travel from Merck Serono, Biogen, Roche, Sanofi Genzyme, Novartis, Mylan; participated on Data Safety Monitoring Board or Advisory Board for Merck Serono, Celgene Bristol Myers Squibb, Biogen, Roche, Sanofi Genzyme. Mannironi A, Pasquali L, Ferrò MT, Liberatore G, Brichetto G, Serrati C, Marinelli F, Carmisciano L, Clerico M, Di Sapio, A, Tassinari T, Visconti V, Perego G, Pizzorno M, Callari G, Cocco E, Frau J, Gazzola P, Repice AM, Schiavetti I, Signoriello E, Stromillo ML, Cordera S, Franciotta D, Iodice R, Lapucci C, Battaglia MA, Gandoglia I have nothing to disclose.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

