Urinary extracellular vesicles contain mature transcriptome enriched in circular and long noncoding RNAs with functional significance in prostate cancer
- PMID: 35527349
- PMCID: PMC9081490
- DOI: 10.1002/jev2.12210
Urinary extracellular vesicles contain mature transcriptome enriched in circular and long noncoding RNAs with functional significance in prostate cancer
Abstract
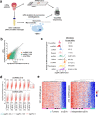
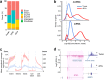
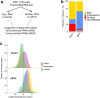
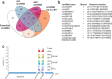
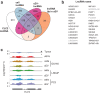
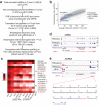
Long noncoding (lnc)RNAs modulate gene expression alongside presenting unexpected source of neoantigens. Despite their immense interest, their ability to be transferred and control adjacent cells is unknown. Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) offer a protective environment for nucleic acids, with pro and antitumourigenic functions by controlling the immune response. In contrast to extracellular nonvesicular RNA, few studies have addressed the full RNA content within human fluids' EVs and have compared them with their tissue of origin. Here, we performed Total RNA-Sequencing on six Formalin-Fixed-Paraffin-Embedded (FFPE) prostate cancer (PCa) tumour tissues and their paired urinary (u)EVs to provide the first whole transcriptome comparison from the same patients. UEVs contain simplified transcriptome with intron-free cytoplasmic transcripts and enriched lnc/circular (circ)RNAs, strikingly common to an independent 20 patients' urinary cohort. Our full cellular and EVs transcriptome comparison within three PCa cell lines identified a set of overlapping 14 uEV-circRNAs characterized as essential for prostate cell proliferation in vitro and 28 uEV-lncRNAs belonging to the cancer-related lncRNA census (CLC2). In addition, we found 15 uEV-lncRNAs, predicted to encode 768 high-affinity neoantigens, and for which three of the encoded-ORF produced detectable unmodified peptides by mass spectrometry. Our dual analysis of EVs-lnc/circRNAs both in urines' and in vitro's EVs provides a fundamental resource for future uEV-lnc/circRNAs phenotypic characterization involved in PCa.
Keywords: CircRNA; EV; TSA; lncRNA; neoantigen.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles published by Wiley Periodicals, LLC on behalf of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amorim, M. G. , Valieris, R. , Drummond, R. D. , Pizzi, M. P. , Freitas, V. M. , Sinigaglia‐Coimbra, R. , Calin, G. A. , Pasqualini, R. , Arap, W. , Silva, I. T. , Dias‐Neto, E. , & Nunes, D. N. (2017). A total transcriptome profiling method for plasma‐derived extracellular vesicles: Applications for liquid biopsies. Scientific Reports, 7, 14395. 10.1038/s41598-017-14264-5 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bachmayr‐Heyda, A. , Reiner, A. T. , Auer, K. , Sukhbaatar, N. , Aust, S. , Bachleitner‐Hofmann, T. , Mesteri, I. , Grunt, T. W. , Zeillinger, R. , & Pils, D. (2015). Correlation of circular RNA abundance with proliferation–exemplified with colorectal and ovarian cancer, idiopathic lung fibrosis, and normal human tissues. Scientific Reports, 5, 8057. 10.1038/srep08057 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barreiro, K. , Dwivedi, Om P. , Leparc, G. , Rolser, M. , Delic, D. , Forsblom, C. , Groop, P. ‐. H. , Groop, L. , Huber, T. B. , Puhka, M. , & Holthofer, H. (2020). Comparison of urinary extracellular vesicle isolation methods for transcriptomic biomarker research in diabetic kidney disease. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 10, e12038. 10.1002/jev2.12038 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

