Computational design of enhanced detoxification activity of a zearalenone lactonase from Clonostachys rosea in acidic medium
- PMID: 35527979
- PMCID: PMC9072336
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04964a
Computational design of enhanced detoxification activity of a zearalenone lactonase from Clonostachys rosea in acidic medium
Abstract
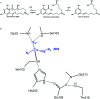
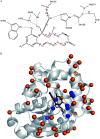
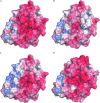
Computational design of pH-activity profiles for enzymes is of great importance in industrial applications. In this research, a computational strategy was developed to engineer the pH-activity profile of a zearalenone lactonase (ZHD101) from Clonostachys rosea to promote its activity in acidic medium. The active site pK a values of ZHD101 were computationally designed by introducing positively charged lysine mutations on the enzyme surface, and the experimental results showed that two variants, M2(D157K) and M9(E171K), increased the catalytic efficiencies of ZHD101 modestly under acidic conditions. Moreover, two variants, M8(D133K) and M9(E171K), were shown to increase the turnover numbers by 2.73 and 2.06-fold with respect to wild type, respectively, though their apparent Michaelis constants were concomitantly increased. These results imply that the active site pK a value change might affect the pH-activity profile of the enzyme. Our computational strategy for pH-activity profile engineering considers protein stability; therefore, limited experimental validation is needed to discover beneficial mutations under shifted pH conditions.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

