Synthesis and compatibility evaluation of versatile mesoporous silica nanoparticles with red blood cells: an overview
- PMID: 35528069
- PMCID: PMC9074774
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra06127d
Synthesis and compatibility evaluation of versatile mesoporous silica nanoparticles with red blood cells: an overview
Abstract
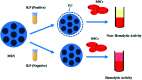
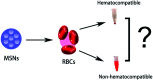
Protean mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs) are propitious candidates over decades for nanoscale drug delivery systems due to their unique characteristics, including (but not limited to) changeable pore size, mesoporosity, high drug loading capacity, and biodegradability. MSNs have been drawing considerable attention as competent, safer and effective drug delivery vehicles day by day by their towering mechanical, chemical and thermal characteristics. Straightforward and easy steps are involved in the synthesis of MSNs at a relatively cheaper cost. This review reports Stober's synthesis, the first proposed synthesis procedure to prepare micron-sized, spherical MSNs, followed by other modifications later on done by scientists. To ensure the safety and compatibility of MSNs with biological systems, the hemocompatibility evaluation of MSNs using human red blood cells (RBCs) is a widely welcomed exercise. Though our main vision of this overview is to emphasize more on the hemocompatibility of MSNs to RBCs, we also brief about the synthesis and widespread applications of multifaceted MSNs. The strike of different parameters of MSNs plays a crucial role concerning the hemolytic activity of MSNs, which also has been discussed here. The inference is derived by centering some feasible measures that can be adopted to cut down or stop the hemolytic activity of MSNs in the future.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Comprehensive Review on Synthesis and Recent Advances.Pharmaceutics. 2018 Aug 6;10(3):118. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics10030118. Pharmaceutics. 2018. PMID: 30082647 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for therapeutic/diagnostic applications.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Jan;109:1100-1111. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.167. Epub 2018 Nov 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 30551360 Review.
-
Impact of shape and pore size of mesoporous silica nanoparticles on serum protein adsorption and RBCs hemolysis.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Feb 26;6(4):2431-8. doi: 10.1021/am404860q. Epub 2014 Feb 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 24460090
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: synthesis, classification, drug loading, pharmacokinetics, biocompatibility, and application in drug delivery.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019 Mar;16(3):219-237. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2019.1575806. Epub 2019 Feb 7. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2019. PMID: 30686075 Review.
-
Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: facile surface functionalization and versatile biomedical applications in oncology.Acta Biomater. 2020 Oct 15;116:1-15. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.09.009. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32911102 Review.
Cited by
-
5-Fluorouracil in Combination with Calcium Carbonate Nanoparticles Loaded with Antioxidant Thymoquinone against Colon Cancer: Synergistically Therapeutic Potential and Underlying Molecular Mechanism.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Aug 25;13(9):1030. doi: 10.3390/antiox13091030. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39334689 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Sintering Temperature of Bioactive Glass Nanoceramics on the Hemolytic Activity and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Erythrocytes.Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020 Apr 3;13(3):201-218. doi: 10.1007/s12195-020-00614-3. eCollection 2020 Jun. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2020. PMID: 32426058 Free PMC article.
-
Application of non-metal nanoparticles, as a novel approach, for improving the stability of blood products: 2011-2021.Prog Biomater. 2022 Jun;11(2):137-161. doi: 10.1007/s40204-022-00188-5. Epub 2022 May 10. Prog Biomater. 2022. PMID: 35536502 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Galactose-decorated liver tumor-specific nanoliposomes incorporating selective BRD4-targeted PROTAC for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy.Heliyon. 2022 Jan 3;8(1):e08702. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e08702. eCollection 2022 Jan. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 35036599 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Non-Modified as Well as Surface-Modified SiO2 Nanoparticles on Red Blood Cells, Biological and Model Membranes.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 21;24(14):11760. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411760. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511517 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martinez D. S. T. Paula A. J. Fonseca L. C. Luna L. A. V. Silveira C. P. Duran N. Alves O. L. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015:4595–4602. doi: 10.1002/ejic.201500573. - DOI
-
- Joglekar M. Roggers R. A. Zhao Y. Trewyn B. G. RSC Adv. 2013;3:2454–2461. doi: 10.1039/C2RA22264G. - DOI
-
- Wani A. S., Formulation Development of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles as an Injectable Delivery System, Wayne State University, 2013, p. 713
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

