Super U-Net: a modularized generalizable architecture
- PMID: 35528144
- PMCID: PMC9070860
- DOI: 10.1016/j.patcog.2022.108669
Super U-Net: a modularized generalizable architecture
Abstract
Objective: To develop and validate a novel convolutional neural network (CNN) termed "Super U-Net" for medical image segmentation.
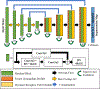
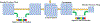
Methods: Super U-Net integrates a dynamic receptive field module and a fusion upsampling module into the classical U-Net architecture. The model was developed and tested to segment retinal vessels, gastrointestinal (GI) polyps, skin lesions on several image types (i.e., fundus images, endoscopic images, dermoscopic images). We also trained and tested the traditional U-Net architecture, seven U-Net variants, and two non-U-Net segmentation architectures. K-fold cross-validation was used to evaluate performance. The performance metrics included Dice similarity coefficient (DSC), accuracy, positive predictive value (PPV), and sensitivity.
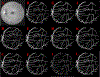
Results: Super U-Net achieved average DSCs of 0.808±0.0210, 0.752±0.019, 0.804±0.239, and 0.877±0.135 for segmenting retinal vessels, pediatric retinal vessels, GI polyps, and skin lesions, respectively. The Super U-net consistently outperformed U-Net, seven U-Net variants, and two non-U-Net segmentation architectures (p < 0.05).
Conclusion: Dynamic receptive fields and fusion upsampling can significantly improve image segmentation performance.
Keywords: U-Net; dynamic receptive field; fusion upsampling; image segmentation.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
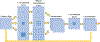
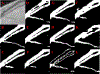



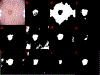
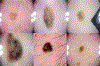
References
-
- Lifeng Qiao YZ, Zhou Hui, “Diabetic Retinopathy Detection Using Prognosis of Microaneurysm and Early Diagnosis System for Non-Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Deep Learning Algorithms,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 104292–104302, 2020.
-
- Lennox Hoyte WY, Brubaker Linda, Fielding Julia R., Lockhard Mark E., Heilbrun Marta E., Brown Morton B., Warfield Simon K., “Segmentations of MRI Images of the Female PelvicFloor: A Study of Inter- and Intra-reader Reliability,” Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging, vol. 33, pp. 684–691, 2011. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Frezghi Habte SB, Shay Keren1, Doyle Timothy C,, Levin Craig S, Paik David S, “In situ study of the impact of inter- and intra-reader variability on region of interest (ROI) analysis in preclinical molecular imaging,” American journal of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging, vol. 3, pp. 175–181, 2013. - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
