Biological Effect of Quercetin in Repairing Brain Damage and Cerebral Changes in Rats: Molecular Docking and In Vivo Studies
- PMID: 35528172
- PMCID: PMC9071882
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8962149
Biological Effect of Quercetin in Repairing Brain Damage and Cerebral Changes in Rats: Molecular Docking and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
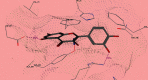
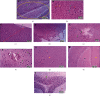
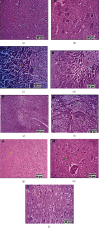
This study examined the protective effect of quercetin against high-altitude-induced brain damage in rats. A molecular docking study was performed to investigate the potential effect of quercetin in reducing brain damages through its ability to target the oxidative stress enzymes. Biomarker assessment screening assays were also performed then followed by in vivo studies. Three groups of rats were divided into the control group, an untreated animal model group with induced brain damage, and finally, the quercetin treated group that received quercetin dose equal to 20 mg/kg of their body weights. Molecular docking studies and biomarker assessment screening assays proved the potential effect of quercetin to affect the level of representative biomarkers glutathione (GSH), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione-S-transferase (GST), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), and malondialdehyde (MDA). Additionally, the protective effect of quercetin against high altitude, low pressure, and low oxygen was also investigated by exploring the brain histopathology of experimental rats. Brain damage was observed in the untreated animal model group. After treatment with quercetin, the cerebral edema in the brain tissues was improved significantly, confirming the protective effects of quercetin. Therefore, quercetin can be used as a natural food additive to protect from the highaltitude-induced brain damage.
Copyright © 2022 Ahmed B. M. Mehany et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative effect of pioglitazone, quercetin and hydroxy citric acid on the status of lipid peroxidation and antioxidants in experimental non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014 Feb;65(1):67-74. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24622831
-
Quercetin attenuates lindane induced oxidative stress in Wistar rats.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Jun;39(6):6895-905. doi: 10.1007/s11033-012-1516-0. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 22302394
-
Monosodium glutamate-induced oxidative damage and genotoxicity in the rat: modulatory role of vitamin C, vitamin E and quercetin.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2006 May;25(5):251-9. doi: 10.1191/0960327106ht621oa. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2006. PMID: 16758767
-
Influence of quercetin on haematological indices and biomarkers of oxidative stress in the serum of rats exposed to atrazine.Afr J Med Med Sci. 2010 Dec;39 Suppl:81-8. Afr J Med Med Sci. 2010. PMID: 22416648
-
Oxidative stress and brain mitochondria swelling induced by endosulfan and protective role of quercetin in rat.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015 May;22(10):7776-81. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3885-5. Epub 2015 Feb 28. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2015. PMID: 25721524
Cited by
-
Phytochemistry, Bioactivities of Metabolites, and Traditional Uses of Fagopyrum tataricum.Molecules. 2022 Oct 20;27(20):7101. doi: 10.3390/molecules27207101. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36296694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of Some Heterocyclic Molecules as Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 (BMP-2)-Inducible Kinase Inhibitors: Virtual Screening, ADME Properties, and Molecular Docking Simulations.Molecules. 2022 Aug 30;27(17):5571. doi: 10.3390/molecules27175571. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36080338 Free PMC article.
-
Neural regeneration ability of Polypyrrole-Collagen-Quercetin composite in the spinal cord injury.Regen Ther. 2023 Jun 14;24:85-93. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2023.05.010. eCollection 2023 Dec. Regen Ther. 2023. PMID: 37334243 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic potential of natural products in inflammation: underlying molecular mechanisms, clinical outcomes, technological advances, and future perspectives.Inflammopharmacology. 2023 Dec;31(6):2857-2883. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01366-y. Epub 2023 Nov 11. Inflammopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 37950803 Review.
-
Imperatorin as an activator of Nrf2/ARE in mercury-induced brain damage based on rat model study, molecular docking, and molecular simulation approaches.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun 11. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-04280-y. Online ahead of print. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40498094
References
-
- Hackett P. H. High-altitude medicine. Wilderness medicine . 2007:2–43.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

