The Genetic Landscape of Ocular Adnexa MALT Lymphoma Reveals Frequent Aberrations in NFAT and MEF2B Signaling Pathways
- PMID: 35528192
- PMCID: PMC9075502
- DOI: 10.1158/2767-9764.crc-21-0022
The Genetic Landscape of Ocular Adnexa MALT Lymphoma Reveals Frequent Aberrations in NFAT and MEF2B Signaling Pathways
Erratum in
-
Correction: The Genetic Landscape of Ocular Adnexa MALT Lymphoma Reveals Frequent Aberrations in NFAT and MEF2B Signaling Pathways.Cancer Res Commun. 2023 Aug 29;3(8):1688. doi: 10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-23-0371. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cancer Res Commun. 2023. PMID: 37649813 Free PMC article.
Abstract
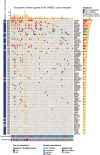
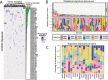
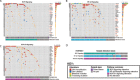
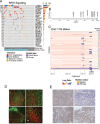
A comprehensive constellation of somatic non-silent mutations and copy number (CN) variations in ocular adnexa marginal zone lymphoma (OAMZL) is unknown. By utilizing whole-exome sequencing in 69 tumors we define the genetic landscape of OAMZL. Mutations and CN changes in CABIN1 (30%), RHOA (26%), TBL1XR1 (22%), and CREBBP (17%) and inactivation of TNFAIP3 (26%) were among the most common aberrations. Candidate cancer driver genes cluster in the B-cell receptor (BCR), NFkB, NOTCH and NFAT signaling pathways. One of the most commonly altered genes is CABIN1, a calcineurin inhibitor acting as a negative regulator of the NFAT and MEF2B transcriptional activity. CABIN1 deletions enhance BCR-stimulated NFAT and MEF2B transcriptional activity, while CABIN1 mutations enhance only MEF2B transcriptional activity by impairing binding of mSin3a to CABIN1. Our data provide an unbiased identification of genetically altered genes that may play a role in the molecular pathogenesis of OAMZL and serve as therapeutic targets.
Keywords: CABIN1; MEF2B; Marginal zone lymphoma; NFAT; Orbital adnexa lymphoma.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE OF CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare no conflicts of interest related to this study
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

