Osteoblast Derived Exosomes Alleviate Radiation- Induced Hematopoietic Injury
- PMID: 35528209
- PMCID: PMC9070646
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.850303
Osteoblast Derived Exosomes Alleviate Radiation- Induced Hematopoietic Injury
Abstract
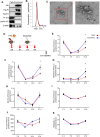
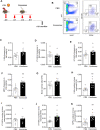
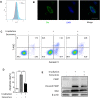
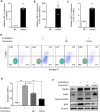
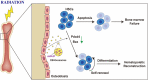
As hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into all hematopoietic lineages, mitigating the damage to hematopoietic stem cells is important for recovery from overdose radiation injury. Cells in bone marrow microenvironment are essential for hematopoietic stem cells maintenance and protection, and many of the paracrine mediators have been discovered in shaping hematopoietic function. Several recent reports support exosomes as effective regulators of hematopoietic stem cells, but the role of osteoblast derived exosomes in hematopoietic stem cells protection is less understood. Here, we investigated that osteoblast derived exosomes could alleviate radiation damage to hematopoietic stem cells. We show that intravenous injection of osteoblast derived exosomes promoted WBC, lymphocyte, monocyte and hematopoietic stem cells recovery after irradiation significantly. By sequencing osteoblast derived exosomes derived miRNAs and verified in vitro, we identified miR-21 is involved in hematopoietic stem cells protection via targeting PDCD4. Collectively, our data demonstrate that osteoblast derived exosomes derived miR-21 is a resultful regulator to radio-protection of hematopoietic stem cells and provide a new strategy for reducing radiation induced hematopoietic injury.
Keywords: apoptosis resistance; hematopoietic injury; irradiation; miR-21; osteoblast derived exosomes.
Copyright © 2022 Xue, Du, Ling, Song, Yuan, Liu, Sun, Li, Zhong, Wang, Yuan, Jin, Liu, Zhao, Li, Xing, Fan, Liu, Pan, Zhen, Zhao, Yang, Li, Chang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Alessio N., Del Gaudio S., Capasso S., Di Bernardo G., Cappabianca S., Cipollaro M., et al. (2015). Low Dose Radiation Induced Senescence of Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Impaired the Autophagy Process. Oncotarget 6 (10), 8155–8166. 10.18632/oncotarget.2692 PubMed Abstract | 10.18632/oncotarget.2692 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alessio N., Esposito G., Galano G., De Rosa R., Anello P., Peluso G., et al. (2017). Irradiation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells with Low and High Doses of Alpha Particles Induces Senescence And/or Apoptosis. J. Cel. Biochem. 118 (9), 2993–3002. 10.1002/jcb.25961 PubMed Abstract | 10.1002/jcb.25961 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arai F., Suda T. (2007). Maintenance of Quiescent Hematopoietic Stem Cells in the Osteoblastic Niche. Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 1106, 41–53. 10.1196/annals.1392.005 PubMed Abstract | 10.1196/annals.1392.005 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arora R., Chawla R., Marwah R., Kumar V., Goel R., Arora P., et al. (2010). Medical Radiation Countermeasures for Nuclear and Radiological Emergencies: Current Status and Future Perspectives. J. Pharm. Bioall Sci. 2 (3), 202–212. 10.4103/0975-7406.68502 PubMed Abstract | 10.4103/0975-7406.68502 | Google Scholar - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai J., Wang Y., Wang J., Zhai J., He F., Zhu G. (2020). Irradiation-induced Senescence of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Aggravates Osteogenic Differentiation Dysfunction via Paracrine Signaling. Am. J. Physiology-Cell Physiol. 318 (5), C1005–c1017. 10.1152/ajpcell.00520.2019 10.1152/ajpcell.00520.2019 | Google Scholar - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

