A Concise Review on the Utilization of Abbreviated Protocol Breast MRI over Full Diagnostic Protocol in Breast Cancer Detection
- PMID: 35528224
- PMCID: PMC9071885
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8705531
A Concise Review on the Utilization of Abbreviated Protocol Breast MRI over Full Diagnostic Protocol in Breast Cancer Detection
Abstract
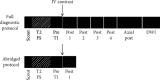
Breast MRI possesses high sensitivity for detecting breast cancer among the current clinical modalities and is an indispensable imaging practice. Breast MRI comprises diffusion-weighted imaging, ultrafast, and T2 weighted and T1 weighted CE (contrast-enhanced) imaging that may be utilized for improving the characterization of the lesions. This multimodal evaluation of breast lesions enables outstanding discrimination between the malignant and benign and malignant lesions. The expanding indications of breast MRI confirm the far superiority of MRI in preoperative staging, especially in the estimation of tumour size and identifying tumour foci in the contralateral and ipsilateral breast. Recent studies depicted that experts can meritoriously utilize this tool for improving breast cancer surgery despite their existence of no significant long term outcomes. For managing the, directly and indirectly, associated screening cost, abbreviated protocols are found to be more beneficial. Further, in some of the patients who were treated with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, breast MRI is utilized for documenting response. It is therefore essential to realise that oncological screening must be easily available, cost-effective, and time-consuming. Earlier detection of this short sequence protocol leads to prior and early breast cancer disease in high risky female populations like women with dense breasts, prehistoric evidence, etc. This proper utilization of AP reduces unnecessary mastectomies. Hence, this review focused on the explorative information for strongly suggesting the benefits of AP breast MRI compared to full diagnostic protocol MRI.
Copyright © 2022 Haytham Al Ewaidat and Mohammad Ayasrah.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest of any type.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Breast MRI: State of the Art.Radiology. 2019 Sep;292(3):520-536. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2019182947. Epub 2019 Jul 30. Radiology. 2019. PMID: 31361209 Review.
-
Ultra-High b-Value Diffusion-Weighted Imaging-Based Abbreviated Protocols for Breast Cancer Detection.Invest Radiol. 2021 Oct 1;56(10):629-636. doi: 10.1097/RLI.0000000000000784. Invest Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34494995
-
Evaluation of Interreader Agreement between Optimized Short and Full Breast MRI Protocols for Screening Breast Cancer in Moderate- and High-Risk Women.Breast Care (Basel). 2025 Mar 5:1-7. doi: 10.1159/000543958. Online ahead of print. Breast Care (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40224347 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy of abbreviated breast MRI protocols using 1.5 T MRI in the preoperative staging of newly diagnosed breast cancers.Clin Imaging. 2023 Sep;101:44-49. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2023.05.016. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Clin Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37295233
-
Fast MRI breast cancer screening - Ready for prime time.Clin Imaging. 2020 Apr;60(2):160-168. doi: 10.1016/j.clinimag.2019.10.013. Epub 2019 Nov 30. Clin Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31927171 Review.
Cited by
-
Invasive Lobular Carcinoma: A Review of Imaging Modalities with Special Focus on Pathology Concordance.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Mar 3;11(5):746. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11050746. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36900751 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of contrast agent on T2-weighted fat-suppressed imaging and diffusion-weighted imaging in the diagnosis of breast tumors.Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024 May 1;14(5):3655-3664. doi: 10.21037/qims-23-1700. Epub 2024 Apr 10. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2024. PMID: 38720833 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mann R. M., van Zelst J. C., Vreemann S., Mus R. D. Is ultrafast or abbreviated breast MRI ready for prime time? Current Breast Cancer Reports . 2019;11(1):9–16. doi: 10.1007/s12609-019-0300-8. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources