Risk Factors for Dupuytren's Contracture: A Case-Control Study
- PMID: 35528327
- PMCID: PMC9071955
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3574037
Risk Factors for Dupuytren's Contracture: A Case-Control Study
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Risk Factors for Dupuytren's Contracture: A Case-Control Study.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9757482. doi: 10.1155/2023/9757482. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38074359 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To study the risk factors of Dupuytren's contracture (DC) and to provide a reference for the clinical prevention and treatment of DC.
Methods: The clinical data of 21 DC patients treated with surgery in Qilu Hospital of Shandong University (Qingdao) from March 2014 to January 2022 were collected. During the same period, 31 subjects who were admitted to the hospital for treatment of finger numbness, difficulty in movement, and other reasons were selected as the control group, and the clinical data of the control group were collected. A case-control study was used to analyze the risk factors for DC. The receiver operating curve (ROC) was used to analyze the efficacy of blood biochemical indexes and coagulation-related indexes in predicting the occurrence of DC.
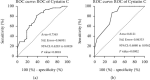
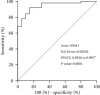
Results: Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that male and diabetes were independent risk factors for the occurrence of DC (HR = 19.69, 95%CI: 3.12-124.19, P = 0.002; HR = 7.61, 95%CI: 1.25-46.47, P = 0.03). The results of the ROC analysis showed that the area under the curve (AUC) for the DC predicted by cystatin C was 0.7565 (95%CI: 0.6203-0.8928, P = 0.0018), and the AUC for the DC predicted by blood chloride level was 0.8121 (95%CI: 0.6880-0.9362, P = 0.0002), the AUC for the DC predicted by fibrinogen was 0.7796 (95%CI: 0.6439-0.9152, P = 0.0007), the AUC for the DC predicted by D-dimer level was 0.8740 (95%CI: 0.7812-0.9669, P < 0.0001), and the AUC for the DC predicted by thrombin time was 0.7803 (95%CI: 0.6411-0.9196, P = 0.0007). The AUC for the DC predicted by the combined detection of cystatin C, blood chloride, fibrinogen, D-dimer, and thrombin time was 0.9441 (95%CI: 0.8926-0.9957, P < 0.001).
Conclusion: Male and diabetes are independent risk factors for the occurrence of DC. Combined detection of cystatin C, blood chloride, fibrinogen, D-dimer, and thrombin time has a certain value in predicting the occurrence of DC.
Copyright © 2022 Liangxiao Zheng et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Computational Model of Blood D-Dimer, Cystatin C, and CRP Levels Predicts the Risk of Intracranial Aneurysms and their Rupture.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022 Nov 18;2022:2216509. doi: 10.1155/2022/2216509. eCollection 2022. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9781203. doi: 10.1155/2023/9781203. PMID: 36438687 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Dupuytren's Contracture: Incidence of Injury-Induced Cases and Specific Clinical Expression.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Jun 30;56(7):323. doi: 10.3390/medicina56070323. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32629785 Free PMC article.
-
[The predictive value of dynamic changes of coagulation function for the occurrence and progression of isolated distal deep vein thrombosis of lower limbs in patients with acute brain injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Jun;33(6):721-726. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20210323-00427. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 34296693 Chinese.
-
A study of the repeatability of the diagnosis of Dupuytren's contracture and its prevalence in the grampian region.J Hand Surg Br. 1993 Apr;18(2):258-61. doi: 10.1016/0266-7681(93)90124-x. J Hand Surg Br. 1993. PMID: 8501390 Review.
-
[Etiology of Dupuytren's contracture].Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2008 Jul-Aug;73(4):232-5. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2008. PMID: 18847012 Review. Polish.
Cited by
-
Retracted: Risk Factors for Dupuytren's Contracture: A Case-Control Study.Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9757482. doi: 10.1155/2023/9757482. eCollection 2023. Comput Intell Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38074359 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

