Efficient release of immunocaptured cells using coiled-coils in a microfluidic device
- PMID: 35528412
- PMCID: PMC9071837
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03871j
Efficient release of immunocaptured cells using coiled-coils in a microfluidic device
Abstract
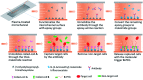
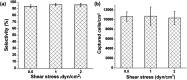
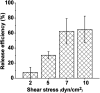
Label-free and affinity-based cell separation allows highly specific cell capture through simple procedures, but it remains a major challenge to efficiently release the captured cells without changing their structure, phenotype, and function. We report a microfluidic platform for label-free immunocapture of target cells and efficient release of the cells with minimal biochemical and biophysical perturbations. The method capitalizes on self-assembly of a pair of heterodimerizing coiled-coils, A and B. Target cells are captured in microchannels functionalized with an antibody and A and efficiently released by a liquid flow containing B-PEG (a conjugate of B and polyethylene glycol) at a controlled, low shear stress. The released cells have no antibodies attached or endogenous surface molecules cleaved. In a model system, human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) were isolated from a mixture of HUVECs and human ovarian carcinoma cells. The capture selectivity, capture capacity, and release efficiency were 96.3% ± 1.8%, 10 735 ± 1897 cells per cm2, and 92.5% ± 3.8%, respectively, when the flow was operated at a shear stress of 1 dyn cm-2. The method can be readily adapted for isolation of any cells that are recognizable by a commercially available antibody, and B-PEG is a universal cell-releasing trigger.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Efficient Release of Affinity-Captured Cells Using a Coiled-Coil-Based Molecular Trigger.Macromol Biosci. 2017 Mar;17(3). doi: 10.1002/mabi.201600330. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Macromol Biosci. 2017. PMID: 27739252
-
Controlled viable release of selectively captured label-free cells in microchannels.Lab Chip. 2011 Dec 7;11(23):3979-89. doi: 10.1039/c1lc20487d. Epub 2011 Oct 14. Lab Chip. 2011. PMID: 22002065 Free PMC article.
-
Erratum: Preparation of Poly(pentafluorophenyl acrylate) Functionalized SiO2 Beads for Protein Purification.J Vis Exp. 2019 Apr 30;(146). doi: 10.3791/6328. J Vis Exp. 2019. PMID: 31038480
-
Ginkgolide B inhibits platelet and monocyte adhesion in TNFα-treated HUVECs under laminar shear stress.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Jul 20;18(1):220. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2284-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30029641 Free PMC article.
-
Efficient elusion of viable adhesive cells from a microfluidic system by air foam.Biomicrofluidics. 2014 Aug 13;8(5):052001. doi: 10.1063/1.4893348. eCollection 2014 Sep. Biomicrofluidics. 2014. PMID: 25332725 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Microfluidic isolation and release of live disseminated breast tumor cells in bone marrow.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 12;20(3):e0319392. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319392. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40073025 Free PMC article.
-
Past, Present, and Future of Affinity-based Cell Separation Technologies.Acta Biomater. 2020 Aug;112:29-51. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.05.004. Epub 2020 May 19. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32442784 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

