Modulation of JNK-1/ β-catenin signaling by Lactobacillus casei, inulin and their combination in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in mice
- PMID: 35528422
- PMCID: PMC9071812
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04388h
Modulation of JNK-1/ β-catenin signaling by Lactobacillus casei, inulin and their combination in 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon cancer in mice
Abstract
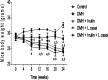
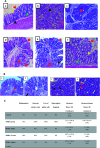
Colon cancer is a complex disease that involves numerous genetic alterations that change the normal colonic mucosa into invasive adenocarcinoma. In the current study, the protective effects of inulin (prebiotic), Lactobacillus casei (L. casei, probiotic) and their combination (synbiotic) on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine (DMH)-induced colon cancer in male Swiss mice were evaluated. Animals were divided into: Control group, DMH-treated group, DMH plus inulin, DMH plus L. casei and DMH plus inulin plus L. casei-treated groups. Fecal microbiome analysis, biochemical measurements, histopathological examination of the colon tissues, immunostaining and Western blotting analysis of β-catenin, GSK3β and JNK-1 were performed. The prebiotic-, probiotic- and synbiotic-treated groups showed decreased levels of carcinoembryonic antigen and a lower number of aberrant crypt foci compared to the DMH-treated group with the synbiotic group exhibiting a superior effect. Furthermore, all treatments showed a body weight-reducing effect. Administration of inulin, L. casei or their combination increased the expression level of phospho-JNK-1 while they decreased the expression level of β-catenin and phospho-GSK3β. Remarkably, L. casei treatment resulted in enrichment of certain beneficial bacterial genera i.e. Akkermansia and Turicibacter. Therefore, administration of L. casei and inulin as a synbiotic combination protects against colon cancer in mice.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Synbiotic (Lactobacillus rhamnosus+Lactobacillus acidophilus+inulin) attenuates oxidative stress and colonic damage in 1,2 dimethylhydrazine dihydrochloride-induced colon carcinogenesis in Sprague-Dawley rats: a long-term study.Eur J Cancer Prev. 2014 Nov;23(6):550-9. doi: 10.1097/CEJ.0000000000000054. Eur J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 25025584
-
Protective Effect of Lactobacillus casei on DMH-Induced Colon Carcinogenesis in Mice.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2017 Jun;9(2):163-171. doi: 10.1007/s12602-017-9253-2. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2017. PMID: 28316010
-
Co-administration of a probiotic strain Lactobacillus plantarum LS/07 CCM7766 with prebiotic inulin alleviates the intestinal inflammation in rats exposed to N,N-dimethylhydrazine.Int Immunopharmacol. 2015 Feb;24(2):361-368. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2014.12.022. Epub 2014 Dec 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25536541
-
Probiotic Dahi containing Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum modulates the formation of aberrant crypt foci, mucin-depleted foci, and cell proliferation on 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colorectal carcinogenesis in Wistar rats.Rejuvenation Res. 2014 Aug;17(4):325-33. doi: 10.1089/rej.2013.1537. Rejuvenation Res. 2014. PMID: 24524423
-
Yacon (Smallanthus sonchifolius) and Lactobacillus acidophilus CRL 1014 reduce the early phases of colon carcinogenesis in male Wistar rats.Food Res Int. 2015 Aug;74:48-54. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.04.034. Epub 2015 Apr 24. Food Res Int. 2015. PMID: 28412002
Cited by
-
An Update on the Effects of Probiotics on Gastrointestinal Cancers.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 21;12:680400. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.680400. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34992527 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selenium-Enriched Lactiplantibacillus plantarum ZZU 8-12 Regulates Intestinal Microbiota and Inhibits Acute Liver Injury.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025 Jan 28. doi: 10.1007/s12602-025-10459-9. Online ahead of print. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2025. PMID: 39875778
-
Gut Microbiota: Influence on Carcinogenesis and Modulation Strategies by Drug Delivery Systems to Improve Cancer Therapy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Mar 9;8(10):2003542. doi: 10.1002/advs.202003542. eCollection 2021 May. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34026439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Characteristics of Inulin and Microcrystalline Cellulose and Their Effect on Ameliorating Colitis and Altering Colonic Microbiota in Dextran Sodium Sulfate-Induced Colitic Mice.ACS Omega. 2022 Mar 23;7(13):10921-10932. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06552. eCollection 2022 Apr 5. ACS Omega. 2022. PMID: 35415348 Free PMC article.
-
Association between Probiotics and Modulation of Gut Microbial Community Composition in Colorectal Cancer Animal Models: A Systematic Review (2010-2021).Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2023 Sep 9;2023:3571184. doi: 10.1155/2023/3571184. eCollection 2023. Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37719797 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Liu C. et al., Phytic acid improves intestinal mucosal barrier damage and reduces serum levels of proinflammatory cytokines in a 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced rat colorectal cancer model. Br. J. Nutr. 2018;120:121–130. doi: 10.1017/s0007114518001290. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518001290. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

