Ex vivo and in vitro inhibitory potential of Kava extract on monoamine oxidase B activity in mice
- PMID: 35528470
- PMCID: PMC9072822
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.07.002
Ex vivo and in vitro inhibitory potential of Kava extract on monoamine oxidase B activity in mice
Abstract
Background and aim: This study investigated the effect of Kava extract (Piper methysticum), a medicinal plant that has been worldly used by its anxiolytic effects, on monoamine oxidase (MAO) activity of mice brain after 21 days of treatment as well as anxiolytic and locomotor behavior. Furthermore, the in vitro inhibitory profile of Kava extract on MAO-B activity of mouse brain was evaluated.
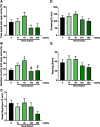
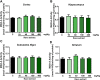
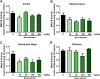
Experimental procedure: Mice were treated with Kava extract (10, 40, 100 and 400 mg/kg) for 21 days by gavage. After behavioral analysis (plus maze test and open field), MAO activity in different mouse brain structures (cortex, hippocampus, region containing the substantia nigra and striatum) were performed. MAO-B inhibitory profile was characterized in vitro.
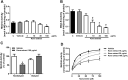
Results: The treatment with Kava extract (40 mg/kg) increased the percentage of entries of mice into the open arms. Ex vivo analysis showed an inhibition on MAO-B activity caused by Kava extract in cortex (10 mg/kg) and in the region containing the substantia nigra (10 and 100 mg/kg). In vitro, Kava extract also reversibly inhibited MAO-B activity with IC50 = 14.62 μg/mL and, increased Km values at the concentrations of 10 and 30 μg/mL and decreased Vmax value at 100 μg/mL.
Conclusion: Kava extract showed different effects on MAO-B isoform depending on the brain structure evaluated. Therefore, the use of Kava extract could be promissory in pathologies where MAO-B is the pharmacological target.
Keywords: 4-HQ, 4-hydroxyquinoline; 5-HT, serotonin; AMPH, amphetamine; Anxiety; CEUA, Ethic Committee on Animal Use; CNS, central nervous system; CONCEA, National Council of Control of Animal Experimentation; DA, dopamine; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; HPLC, High performance liquid chromatography; Kynuramine; MAO, Monoamine oxidase; NE, norepinephrine; Open field; Piper methysticum; Plus maze.
© 2021 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare there are no potential financial, personal, or otherwise conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sarris J., Scholey A., Schweitzer I., et al. The acute effects of kava and oxazepam on anxiety, mood, neurocognition; and genetic correlates: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Hum Psychopharmacol. 2012;27(3):262–269. - PubMed
-
- Jamieson D.D., Duffield P.H. The antinociceptive actions of kava components IN mice. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 1990;17(7):495–507. - PubMed
-
- Cairney S., Maruff P., Clough A.R. The neurobehavioural effects of kava. Aust N Z J Psychiatr. 2002;36(5):657–662. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
