Anti-hypotensive effect of "Yahom Navakot" in rats with orthostatic hypotension
- PMID: 35528473
- PMCID: PMC9072801
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.08.002
Anti-hypotensive effect of "Yahom Navakot" in rats with orthostatic hypotension
Abstract
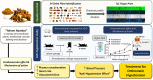
Background and aim: Yahom Navakot (YN), is a Thai traditional medicine, consisting of 54 plants, for treating fainting and dizziness. Thus, YN might relieve orthostatic hypotension (OH) symptoms, but its therapeutic action is unclear. Therefore, this study evaluated YN in OH rats, using a head-up tilt test (HUT).
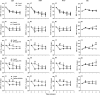
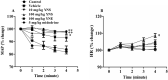
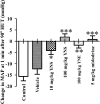
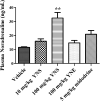
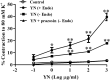
Experimental procedure: Rats were anesthetized, and OH induced via a 90oHUT, before and after administering vehicle, a YN powder suspension (10, 100 mg/kg), a YN aqueous extract (100 mg/kg), and midodrine (5 mg/kg). The systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), mean arterial blood pressure (MAP), pulse pressure (PP) and heart rate (HR) were determined via the carotid artery. Plasma noradrenaline (NA) was evaluated. YN-induced vasoconstriction of isolated rat aorta rings was determined using organ bath technique.
Results and conclusion: Baseline BP increased with the 100 mg/kg YN powder suspension, the YN aqueous extract or midodrine, while HR decreased, compared with vehicle and control. 90oHUT rapidly reduced SBP, DPB and MAP, but increased HR, for control and vehicle-treated groups, but BP was steady with the 100 mg/kg YN powder suspension, the YN aqueous extract or midodrine. The 90oHUT-increase in HR was most pronounced with the 100 mg/kg YN powder suspension (the traditional formulation). This accords with increased plasma NA. YN also induced vasoconstriction in rat aorta via α1-receptor activation. Thus, the anti-hypotensive action of YN involved a stimulating effect on the heart and blood vessels via sympathetic activation. The results support the traditional use of YN and demonstrated the effectiveness of YN for OH prevention.
Keywords: BP, blood pressure; Blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HR, heart rate; HUT, head-up tilt test; Head-up tilt; MAP, mean arterial blood pressure; NA, noradrenaline; OH, orthostatic hypotension; Orthostatic hypotension; PP, pulse pressure; Quality control; SBP, systolic blood pressure; YN, Yahom Navakot; Yahom Navakot.
© 2021 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

Similar articles
-
[Effects of octreotide on experimental orthostatic neurogenic hypotension].Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1996 Aug;89(8):1097-1101. Arch Mal Coeur Vaiss. 1996. PMID: 8949386 French.
-
What is the minimum duration of head-up tilt necessary to detect orthostatic hypotension?Clin Auton Res. 2005 Apr;15(2):71-5. doi: 10.1007/s10286-005-0246-y. Clin Auton Res. 2005. PMID: 15834762 Clinical Trial.
-
Norepinephrine and epinephrine responses during orthostatic intolerance in healthy elderly men.Jpn J Physiol. 2000 Feb;50(1):59-66. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.50.59. Jpn J Physiol. 2000. PMID: 10866698
-
Effects of octreotide on experimental neurogenic orthostatic hypotension in anaesthetized dogs.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1997;11(3):237-44. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-8206.1997.tb00191.x. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 1997. PMID: 9243255
-
Effect of Short-Term Oral Administration of Phikud Navakot in Rats.J Med Assoc Thai. 2015 Nov;98 Suppl 10:S52-60. J Med Assoc Thai. 2015. PMID: 27276833
Cited by
-
Lotus seed (Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn.) extract at low dose ameliorates reproductive dysfunction in l-NAME-induced hypertension and oxidative stress in male rats.J Tradit Complement Med. 2024 May 4;15(4):404-413. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2024.05.001. eCollection 2025 Jul. J Tradit Complement Med. 2024. PMID: 40677545 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jariyapongskul A., Pathumraj S., Niimi H. Effects of Yahom on the regional cerebral blood flow in rat using fluorescence videomicroscopy. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2006;34(1-2):139–144. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
