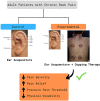
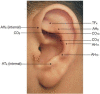
Effects of ear acupuncture combined with cupping therapy on severity and threshold of chronic back pain and physical disability: A randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 35528479
- PMCID: PMC9072818
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2021.07.008
Effects of ear acupuncture combined with cupping therapy on severity and threshold of chronic back pain and physical disability: A randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background and aim: Chronic back pain causes physical, functional, and emotional disabilities. Traditional Chinese Medicine therapies have been shown as interventions to treat chronic back pain. The present study aimed to clinically evaluate the effects of ear acupuncture combined with cupping therapy on people with chronic back pain.
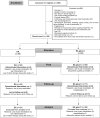
Experimental procedure: We conducted an open-label, randomized, parallel-group controlled clinical trial. Following the CONSORT statement recommendations, 198 participants were randomized into 'ear acupuncture' and 'ear acupuncture and cupping therapy' groups. Data were collected in three different points; before the first session (initial) with the patient, after the last session (final), and seven days after the end of the treatment (follow-up). The Brief Pain Inventory, a digital algometer, and the Rolland Morris Disability Questionnaire were used for data collection. Generalized Estimation Equation model was used to examine the association between the interventions and the primary outcome pain severity.
Results: Pain severity, pressure pain threshold, and physical disability improved over time in both groups. However, for the patients being treated with both ear acupuncture and cupping therapy, significant changes were seen in pain severity, pain relief, and physical disabilities between the initial and final sessions. For the 'ear acupuncture and cupping therapy' group, significant changes were also seen for pain relief and physical disability in the follow-up session.
Conclusion: Ear acupuncture combined with cupping therapy was shown to be more effective in the treatment of chronic back pain when compared to treatment using only ear acupuncture.
Keywords: Back pain; Chronic pain; Clinical trial; Cupping therapy; Ear acupuncture.
© 2021 Center for Food and Biomolecules, National Taiwan University. Production and hosting by Elsevier Taiwan LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of Ear Acupuncture plus Dry Cupping on Activities and Quality of Life in the Adults with Chronic Back Pain: a Randomized Trial.J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2022 Apr 30;15(2):130-142. doi: 10.51507/j.jams.2022.15.2.130. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2022. PMID: 35770580 Clinical Trial.
-
Contribution of Chinese and French ear acupuncture for the management of chronic back pain: A randomised controlled trial.J Clin Nurs. 2019 Nov;28(21-22):3796-3806. doi: 10.1111/jocn.14983. Epub 2019 Aug 9. J Clin Nurs. 2019. PMID: 31237981 Clinical Trial.
-
Single Cupping Thearpy Session Improves Pain, Sleep, and Disability in Patients with Nonspecific Chronic Low Back Pain.J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2020 Apr;13(2):48-52. doi: 10.1016/j.jams.2019.11.004. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Acupunct Meridian Stud. 2020. PMID: 31760207
-
Cupping therapy versus acupuncture for pain-related conditions: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials and trial sequential analysis.Chin Med. 2017 Jul 24;12:21. doi: 10.1186/s13020-017-0142-0. eCollection 2017. Chin Med. 2017. PMID: 28770000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complementary and alternative therapies for back pain II.Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2010 Oct;(194):1-764. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Full Rep). 2010. PMID: 23126534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Auriculotherapy for reducing chronic spinal pain in health workers: a clinical trial.Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2023 Jun 19;31:e3953. doi: 10.1590/1518-8345.6641.3953. eCollection 2023. Rev Lat Am Enfermagem. 2023. PMID: 37341260 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
What are the effects of dry cupping therapy combined with the McKenzie method on clinical outcomes in chronic low back pain? A protocol for a randomized, sham-controlled trial.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025 Jul 2;25(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12906-025-04940-9. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2025. PMID: 40604805 Free PMC article.
-
Antihistamine promotes electroacupuncture analgesia in healthy human subjects: A pilot study.J Tradit Complement Med. 2022 Apr 21;12(5):511-517. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcme.2022.04.003. eCollection 2022 Sep. J Tradit Complement Med. 2022. PMID: 36081814 Free PMC article.
-
Trends and hotspots in cupping therapy research for pain: a bibliometric study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2025 Jul 9;12:1559099. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2025.1559099. eCollection 2025. Front Med (Lausanne). 2025. PMID: 40703280 Free PMC article.
-
Update evidence of effectiveness on pain relieving of cupping therapy: a systematic review and Meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Tradit Chin Med. 2025 Apr;45(2):234-253. doi: 10.19852/j.cnki.jtcm.2025.02.002. J Tradit Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40151111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artioli D.P., Tavares A.L., Bertolini G.R. Auriculotherapy: neurophysiology, points to choose, indications and results on musculoskeletal pain conditions: a systematic review of reviews. Br J Pain. 2019;2(4):356–361. doi: 10.5935/2595-0118.20190065. - DOI
-
- Barker A. 2019. Chronic Pain has arrived in the ICD-11. Retrieved from https://www.iasp-pain.org/PublicationsNews/NewsDetail.aspx?ItemNumber=83....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
