Antimicrobial Efficacy of Chlorhexidine and Herbal Mouth Rinse on Salivary Streptococcus mutans in Children with Mixed Dentition: A Randomized Crossover Study
- PMID: 35528483
- PMCID: PMC9016908
- DOI: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2348
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Chlorhexidine and Herbal Mouth Rinse on Salivary Streptococcus mutans in Children with Mixed Dentition: A Randomized Crossover Study
Abstract
Aim and objective: Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) shows increased resistance to currently available antibiotics and chemotherapeutics. The present study compares the effectiveness of chlorhexidine and Herbal mouth rinse against salivary S. mutans in children with mixed dentition.
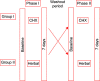
Materials and methods: Subjects (n = 60) with mixed dentition were selected for the study. Caries status was recorded using Nyvard's criteria. Baseline saliva samples were collected and assessed for quantifying S. mutans. Subjects were instructed to rinse their mouths with 0.2 % w/v chlorhexidine and herbal mouth rinse for 7 days. Saliva samples were collected after 7 days and assessed for S. mutans. After a run-in period of 21 days, both the mouth rinses were crossed over according to the Latin square design, and a similar procedure was carried out. Later, determination of mean colony-forming units (CFU/mL) from the saliva samples was done. For statistical analysis, Kolmogorov and Mann-Whitney U tests were applied.
Results: Both the groups showed a significant reduction in S. mutans count, at baseline and 7 days (p = 0.0001), and the reduction of S. mutans count in herbal mouth rinse as compared to chlorhexidine mouth rinse (p = 0.0209) was statistically significant.
Conclusion: Herbal mouth rinse proved to have better antimicrobial efficacy than Chlorhexidine mouth rinse.
How to cite this article: Shah SV, Badakar CM, Hugar SM, et al. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Chlorhexidine and Herbal Mouth Rinse on Salivary Streptococcus mutans in Children with Mixed Dentition: A Randomized Crossover Study. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent 2022;15(1):99-103.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Chlorhexidine; Dental caries; Herbal; Streptococcus mutans.
Copyright © 2022; The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Source of support: Nil Conflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Comparative evaluation of efficacy of 0.2% Chlorhexidine, Listerine and Tulsi extract mouth rinses on salivary Streptococcus mutans count of high school children--RCT.Contemp Clin Trials. 2011 Nov;32(6):802-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cct.2011.06.007. Epub 2011 Jul 6. Contemp Clin Trials. 2011. PMID: 21763461 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative evaluation of antimicrobial efficacy of three different formulations of mouth rinses with multi-herbal mouth rinse.J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2016 Oct-Dec;34(4):315-23. doi: 10.4103/0970-4388.191409. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2016. PMID: 27681394 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparative Evaluation of the Efficacy of Chlorhexidine, Fluoride and the Combined Use of Chlorhexidine and Fluoride Varnishes on Salivary Streptococcus mutans Count in Children with Mixed Dentition: An In Vivo Study.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022 May-Jun;15(3):267-272. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-2360. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2022. PMID: 35991806 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative Evaluation of 0.2 percent Chlorhexidine and Magnetized Water as a Mouth Rinse on Streptococcus mutans in Children.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2011 Sep-Dec;4(3):190-4. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1108. Epub 2011 Apr 15. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2011. PMID: 27678225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antimicrobial Efficacy of Probiotic and Herbal Oral Rinses against Candida albicans in Children: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016 Jan-Mar;9(1):25-30. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1328. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Int J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2016. PMID: 27274151 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sari LN, Fauziah E, Budiardjo SB, et al. Antibacterial and antifungal effectiveness of virgin coconut oil (VCO) mousse against Streptococcus mutans and candida albicans biofilms. J Int Dent Med Res. 2019;12(03):917–922.
-
- Reddy KS, Rapala H, Kethineni B, et al. Prevalence of dental caries in school going children of both urban and rural areas in Mahbubnagar district, Telangana state,(India): An epidemiological study. Int J Pedod Rehabil. 2017;2(01):7–13. doi: 10.4103/2468-8932.205468. - DOI
-
- Jain A, Jain V, Suri SM, et al. Prevalence of dental caries in male children from 3 to 14 years of age of Bundelkhand region, India. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2017;3(04):787–790. doi: 10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph20160730. - DOI
-
- Kulkarni VV, Damle SG. Comparative evaluation of efficacy of sodium fluoride, chlorhexidine and triclosan mouth rinses in reducing the mutans streptococci count in saliva: an in vivo study. J Indian Soc Pedo Prev Dent. 2003;21(03):98–104. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources