Renal Doppler Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Renal Function in Patients with Sepsis
- PMID: 35528533
- PMCID: PMC9071910
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3472405
Renal Doppler Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Renal Function in Patients with Sepsis
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Renal Doppler Ultrasound in the Evaluation of Renal Function in Patients with Sepsis.Appl Bionics Biomech. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9878723. doi: 10.1155/2023/9878723. eCollection 2023. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2023. PMID: 38075157 Free PMC article.
Abstract
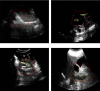
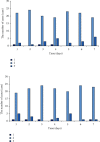
This study was aimed to explore the renal Doppler ultrasound in the evaluation of renal function in patients with sepsis. Fifty patients with sepsis or septic shock were classified into the acute kidney injury (AKI) group (n =25) and the non-AKI group (n =25) according to whether they had AKI. The measurements of renal resistance index (RRI) and power Doppler ultrasound (PDU) were performed on all patients within 7 days of admission to the intensive care unit (ICU). The patient's renal function was assessed. The results showed that the RRI of the two groups showed a slight upward trend over time, and the RRI of the AKI group was higher than that of the non-AKI group. After 7 days in AKI group, the areas under the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of RRI were 0.745, 0.683, 0.729, 0.856, 0.793, 0.819, and 0.836 (P <0.05). There were no statistically considerable differences in areas under ROC curves between the two groups (P >0.05). The grouping of AKI and the time were both fixed effects, and the individual patients were randomized effects. Besides, the linear models were statistically analyzed. The results showed that the differences between the two groups were statistically insignificant (P >0.05). There was no significant difference in the PDU scores measured at different times within 7 days after ICU admission between the two groups (P >0.05). In conclusion, renal Doppler ultrasound had a good adoption effect in the evaluation of the renal function of patients with severe sepsis, which is worth promoting in clinical practice.
Copyright © 2022 Aili Yu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Zhi H. J., Zhao J., Nie S., et al. Prediction of acute kidney injury: the ratio of renal resistive index to semiquantitative power Doppler ultrasound score-a better predictor?: A prospective observational study. Medicine (Baltimore) . 2019;98(21):p. e15465. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000015465. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Simon J. C., Sapozhnikov O. A., Kreider W., Breshock M., Williams J. C., Jr., Bailey M. R. The role of trapped bubbles in kidney stone detection with the color Doppler ultrasound twinkling artifact. Physics in Medicine and Biology . 2018;63(2):p. 025011. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/aa9a2f. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

