Identifying Key MicroRNA Signatures for Neurodegenerative Diseases With Machine Learning Methods
- PMID: 35528544
- PMCID: PMC9068882
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.880997
Identifying Key MicroRNA Signatures for Neurodegenerative Diseases With Machine Learning Methods
Abstract
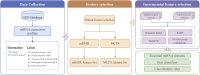
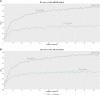
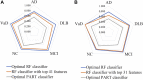
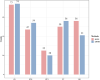
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease, and many other disease types, cause cognitive dysfunctions such as dementia via the progressive loss of structure or function of the body's neurons. However, the etiology of these diseases remains unknown, and diagnosing less common cognitive disorders such as vascular dementia (VaD) remains a challenge. In this work, we developed a machine-leaning-based technique to distinguish between normal control (NC), AD, VaD, dementia with Lewy bodies, and mild cognitive impairment at the microRNA (miRNA) expression level. First, unnecessary miRNA features in the miRNA expression profiles were removed using the Boruta feature selection method, and the retained feature sets were sorted using minimum redundancy maximum relevance and Monte Carlo feature selection to provide two ranking feature lists. The incremental feature selection method was used to construct a series of feature subsets from these feature lists, and the random forest and PART classifiers were trained on the sample data consisting of these feature subsets. On the basis of the model performance of these classifiers with different number of features, the best feature subsets and classifiers were identified, and the classification rules were retrieved from the optimal PART classifiers. Finally, the link between candidate miRNA features, including hsa-miR-3184-5p, has-miR-6088, and has-miR-4649, and neurodegenerative diseases was confirmed using recently published research, laying the groundwork for more research on miRNAs in neurodegenerative diseases for the diagnosis of cognitive impairment and the understanding of potential pathogenic mechanisms.
Keywords: classification algorithm; expression pattern; feature selection; microRNA; neurodegenerative disease.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Guo, Ding, Chen, Feng, Huang and Cai.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

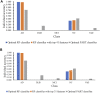
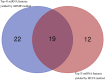
References
-
- Asanomi Y., Shigemizu D., Akiyama S., Sakurai T., Ozaki K., Ochiya T., et al. (2021). Dementia Subtype Prediction Models Constructed by Penalized Regression Methods for Multiclass Classification Using Serum microRNA Expression Data. Sci. Rep. 11, 20947. 10.1038/s41598-021-00424-1 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Breiman L. (2001). Random Forests. Machine Learn. 45, 5–32. 10.1023/a:1010933404324 - DOI
-
- Chawla N. V., Bowyer K. W., Hall L. O., Kegelmeyer W. P. (2002). SMOTE: Synthetic Minority Over-sampling Technique. jair 16, 321–357. 10.1613/jair.953 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

