Trajectory of fine particles removal with diffusiophoresis and thermophoresis in a gas-liquid cross-flow array
- PMID: 35528569
- PMCID: PMC9070523
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04436a
Trajectory of fine particles removal with diffusiophoresis and thermophoresis in a gas-liquid cross-flow array
Abstract
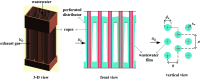
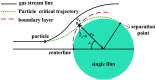
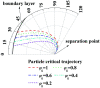
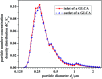
A gas-liquid cross-flow array (GLCA) system is proposed for fine particles (diameter between 0.1 μm and 2.5 μm, simplified as PM2.5) removal in exhaust gas, where the continuous and smooth wastewater films, providing huge specific surface area, each act as independent traps to remove PM2.5. The removal efficiency of PM2.5 is important for evaluating the performance of a GLCA, and the trajectory across the films determines the migration and ultimate fate of PM2.5. An analytical model based on a single film is developed to analyze the critical removal trajectory with diffusiophoresis (DP) and thermophoresis (TP) in the thermal boundary layer to calculate the efficiency, where the role of each force is examined. And experiments with a lab-scale GLCA are carried out with different vapor concentration and temperature gradients to verify the model. They both reveal that the removal efficiency can be increase sharply by increasing the humidity gradient between the bulk gas and film surface, while it increases slowly as temperature gradient increasing. Thus DP and TP have important effects on PM2.5 removal in the GLCA, and DP has a much more important effect than TP. A GLCA with appropriate humidity and temperature gradient can remove PM2.5 in a costly and efficient manner.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures








References
-
- Meij R. Winkel B. T. Fuel Process. Technol. 2004;85:641–656. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2003.11.012. - DOI
-
- Prodia F. Santachiaraa G. Belosia F. Vedernikovb A. Balapanovb D. J. Exposure Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2014;142:40–44.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

