Ginsenoside Rk1 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma by calcium signaling pathway
- PMID: 35528653
- PMCID: PMC9069870
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra05037j
Ginsenoside Rk1 inhibits cell proliferation and promotes apoptosis in lung squamous cell carcinoma by calcium signaling pathway
Abstract
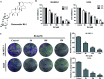
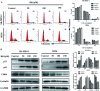
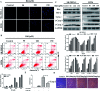
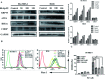
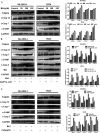
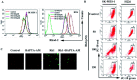
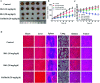
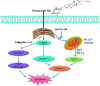
Ginsenoside Rk1 (Rk1) is a rare saponin extracted from Sun Ginseng (SG) and has been shown to have an anti-tumor effect; however, the potential role of its in lung squamous cell carcinoma remains elusive. In this study, we investigated the anti-proliferative activity and involved mechanism of Rk1 against lung squamous cell carcinoma in vitro and in vivo. First, MTT assay, cell colony formation assay and cell cycle assay showed that Rk1 effectively inhibited cell proliferation and colony formation, and induced cell arrest at G1 phase. Following AV/PI staining, JC-10 staining, Western blot and immunohistochemistry indicated that Rk1 induced caspase-dependent apoptosis. In addition, Rk1 induced ER stress, causing the release of Ca2+, resulting in intracellular calcium and mitochondrial calcium overload. Intracellular calcium overload activated the calpain-caspase-12 and calpain-caspase-7-PARP pathways, while mitochondrial calcium overload caused mitochondrial membrane potential reduced, and the release of cytochrome c. BAPTA-AM (Ca2+ scavengers) and calpeptin (calpain inhibitors) significantly attenuated Rk1-induced apoptosis. Moreover, Rk1 significantly inhibited the growth of SK-MES-1 xenograft tumors with low toxic side effects. In summary, this study for the first time demonstrated that Rk1 had significant antitumor effects against lung squamous cell carcinoma and great potential to serve as a novel anticancer agent.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yan L. Yao Y. Wang L. H. Wang M. L. Fu X. H. Detection of CK19, LUNX, and KS1/4 mRNA expression in the peripheral blood for diagnosis of micrometastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer and their clinical implications. Genet. Mol. Res. 2015;14:15090–15095. doi: 10.4238/2015.November.24.17. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Scagliotti G. V., Novello S., Rapetti S. and Papotti M., Current State-of-the-Art Therapy for Advanced Squamous Cell Lung Cancer, American Society of Clinical Oncology Educational Book, 2013, vol. 354 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

