A probabilistic approach toward evaluation of Internet rumor on COVID
- PMID: 35528710
- PMCID: PMC9069954
- DOI: 10.1007/s00500-022-07064-1
A probabilistic approach toward evaluation of Internet rumor on COVID
Abstract
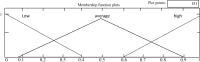
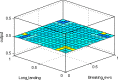
Several people around the world have died from the coronavirus (COVID-19) disease. With the increase in COVID-19 cases, distribution, and deaths, much has occurred regarding the ban on travel, border closure, curfews, and the disturbance in the supply of services and goods. The world economy was severely affected by the spread of the virus. Every day, new discussions and debates started, and more people were in fear. Occasionally, unconfirmed information is shared on social media sites as if it were accurate information. Sometimes, it becomes viral and disturbs people's emotions and beliefs. Fake news and rumors are widespread forms of unconfirmed and false information. This type of news should be tracked speedily to prevent its negative impact on society. An ideal system is the dire need of modern-day society to evaluate the Internet rumors on COVID. Therefore, the current study has considered a probabilistic approach for evaluating the Internet rumors about COVID. The fuzzy logic tool in MATLAB was used for experimental and simulation purposes. The results revealed the effectiveness of the proposed work.
Keywords: Covid 19; Covid pandemic; Fuzzy logic; Internet rumor; Soft computing.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer Nature 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have declared that they have no conflict of interest regarding this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fake news in the age of COVID-19: evolutional and psychobiological considerations.Psychiatriki. 2022 Sep 19;33(3):183-186. doi: 10.22365/jpsych.2022.087. Epub 2022 Jul 19. Psychiatriki. 2022. PMID: 35947862 English, Greek, Modern.
-
Sentiment Analysis of Rumor Spread Amid COVID-19: Based on Weibo Text.Healthcare (Basel). 2021 Sep 27;9(10):1275. doi: 10.3390/healthcare9101275. Healthcare (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34682955 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19-Related Rumor Content, Transmission, and Clarification Strategies in China: Descriptive Study.J Med Internet Res. 2021 Dec 23;23(12):e27339. doi: 10.2196/27339. J Med Internet Res. 2021. PMID: 34806992 Free PMC article.
-
A survey on rumor detection and prevention in social media using deep learning.Knowl Inf Syst. 2023 May 29:1-42. doi: 10.1007/s10115-023-01902-w. Online ahead of print. Knowl Inf Syst. 2023. PMID: 37361373 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Information Overload and Infodemic in the COVID-19 Pandemic.J Pak Med Assoc. 2020 May;70(Suppl 3)(5):S162-S165. doi: 10.5455/JPMA.38. J Pak Med Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32515403 Review.
Cited by
-
A survey of public eye-care behavior and myopia education.Front Public Health. 2025 Feb 18;13:1518956. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1518956. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40046115 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the Accuracy of Two Generated Large Language Models in Identifying Health-Related Rumors or Misconceptions and the Applicability in Health Science Popularization: Proof-of-Concept Study.JMIR Form Res. 2024 Dec 2;8:e63188. doi: 10.2196/63188. JMIR Form Res. 2024. PMID: 39622076 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Abe T, Higashi D, Nishiyama D, Toriumi F, Galam S and Ishii A (2020) The toilet paper issue during the COVID-19 crisis. In: 2020 IEEE/WIC/ACM international joint conference on web intelligence and intelligent agent technology (WI-IAT), pp 655–659
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
