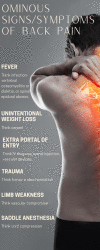
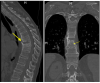
An ominous cause of back pain: Vertebral Osteomyelitis
- PMID: 35528732
- PMCID: PMC9048718
- DOI: 10.52965/001c.32243
An ominous cause of back pain: Vertebral Osteomyelitis
Abstract
The authors present the case of a patient seen for back pain in the emergency department, initially discharged home with a diagnosis of musculoskeletal pain. He returned a week later and was found to have vertebral osteomyelitis based on a thorough neurologic exam. A review of ominous causes of back pain, including the elusive nature of vertebral osteomyelitis/diskitis is discussed.
Keywords: case report; diskitis; vertebral osteomyelitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lumbar vertebral diskitis-osteomyelitis with mycotic abdominal aortic aneurysm caused by Streptococcus mitis.Radiol Case Rep. 2024 Apr 18;19(7):2719-2723. doi: 10.1016/j.radcr.2024.02.039. eCollection 2024 Jul. Radiol Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38680736 Free PMC article.
-
Percutaneous vertebral body cement augmentation for back pain related to occult osteomyelitis/diskitis.Orthopedics. 2011 Nov 9;34(11):e788-92. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20110922-31. Orthopedics. 2011. PMID: 22049968
-
Missed Opportunities for Diagnosing Vertebral Osteomyelitis Caused by Influential Cognitive Biases.Am J Case Rep. 2022 Jun 22;23:e936058. doi: 10.12659/AJCR.936058. Am J Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 35729859 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnosis and treatment of Fusobacterium nucleatum discitis and vertebral osteomyelitis: case report and review of the literature.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013 Jan 15;38(2):E120-2. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0b013e31827b4d61. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2013. PMID: 23132536 Review.
-
Multilevel diskitis and vertebral osteomyelitis after diskography.Orthopedics. 2009 Jan;32(1):60. doi: 10.3928/01477447-20090101-16. Orthopedics. 2009. PMID: 19226022 Review.
Cited by
-
The Invasive Management of Pain: Diagnosis and New Treatment Options.Cureus. 2023 Jul 31;15(7):e42717. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42717. eCollection 2023 Jul. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37654942 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- 1. Deyo RA, Mirza SK, Martin BI. Back pain prevalence and visit rates: Estimates from U.S national surveys, 2002. Spine. 2006;31(23):2724-2727. doi:10.1097/01.brs.0000244618.06877.cd - PubMed
-
- 2. Hart LG, Deyo RA, Cherkin DC. Physician office visits for low back pain. Frequency, clinical evaluation, and treatment patterns from a U.S. national survey. Spine. 1995;20(1):11-19. doi:10.1097/00007632-199501000-00003 - PubMed
-
- 3. Deyo RA, Weinstein JN. Low back pain. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(5):363-370. doi:10.1056/nejm200102013440508 - PubMed
-
- 4. Chenoweth CE, Bassin BS, Mack MR, et al. Vertebral Osteomyelitis, Discitis, and Spinal Epidural Abscess in Adults [Internet]. Michigan Medicine University of Michigan; 2018. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547443/ - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources