Impact of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Deprivation on Pain Behaviour and Oxidative Stress in the Thalamus: Role of Tualang Honey Supplementation
- PMID: 35528807
- PMCID: PMC9036926
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2022.29.2.7
Impact of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Deprivation on Pain Behaviour and Oxidative Stress in the Thalamus: Role of Tualang Honey Supplementation
Abstract
Background: Insufficient sleep alters the body's physiological functions. This study investigated whether oxidative stress (OS) in the thalamus was correlated with the pain behaviour score in the rapid eye movement (REM) sleep-deprived rat model.
Methods: Four groups of Sprague-Dawley rats were included in the study (n = 6): i) control; ii) REM sleep-deprived rats for 72 h (REMsd); iii) REM sleep-deprived rats for 72 h pretreated with Tualang honey (REMsd-H) and iv) tank control (TC). Following the intervention, 1% formalin was injected on the right hind paw and pain behaviour was recorded for 1 h. OS markers of glutathione (GSH), glutathione reductase (GR), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in the thalamus were measured.
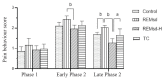
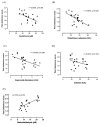
Results: REM sleep deprivation increased pain behaviour scores in phase II of the formalin test with decreased GSH, GR, SOD and CAT. The MDA level was significantly higher in the REMsd compared to REMsd-H. There was an inverse correlation between pain behaviour scores and GSH, GR and SOD levels. A positive correlation was found between the pain behaviour score and the MDA level.
Conclusion: OS levels were significantly correlated with the pain behaviour score in the REMsd rats. Tualang honey administration reduced pain behaviour score and OS in the thalamus.
Keywords: REM sleep deprivation; Tualang honey; oxidative stress biomarkers; pain behaviour score.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sleep Deprivation-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Models: A Scoping Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;12(8):1600. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081600. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627596 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Review of the Reciprocal Relationship Between Sleep Deprivation and Chronic Pain: The Role of Oxidative Stress.J Pain Res. 2024 May 20;17:1785-1792. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S455621. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38799272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipid peroxidation in the descending thoracic aorta of rats deprived of REM sleep using the inverted flowerpot technique.Exp Physiol. 2020 Aug;105(8):1223-1231. doi: 10.1113/EP088667. Epub 2020 Jun 30. Exp Physiol. 2020. PMID: 32539237
-
Antioxidant protection of Malaysian tualang honey in pancreas of normal and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2010 Sep;71(4):291-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ando.2010.03.003. Epub 2010 Apr 15. Ann Endocrinol (Paris). 2010. PMID: 20398890
-
Changes in monoamines and their metabolite concentrations in REM sleep-deprived rat forebrain nuclei.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996 Jun;54(2):385-91. doi: 10.1016/0091-3057(95)02072-1. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 1996. PMID: 8743599
Cited by
-
Sleep Deprivation-Induced Oxidative Stress in Rat Models: A Scoping Systematic Review.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Aug 11;12(8):1600. doi: 10.3390/antiox12081600. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627596 Free PMC article.
-
Medicinal activities of Tualang honey: a systematic review.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024 Oct 4;24(1):358. doi: 10.1186/s12906-024-04664-2. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2024. PMID: 39367403 Free PMC article.
-
A Narrative Review of the Reciprocal Relationship Between Sleep Deprivation and Chronic Pain: The Role of Oxidative Stress.J Pain Res. 2024 May 20;17:1785-1792. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S455621. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 38799272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic REM sleep deprivation leads to manic- and OCD-related behaviors, and decreases hippocampal BDNF expression in female rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024 Jul;241(7):1345-1363. doi: 10.1007/s00213-024-06566-0. Epub 2024 Mar 2. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2024. PMID: 38430395
-
Honey on brain health: A promising brain booster.Front Aging Neurosci. 2023 Jan 17;14:1092596. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.1092596. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36733498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ajao F. Effects of rapid eye movement sleep deprivation on pain perception level in male Wistar rats. Asian J Biomed Pharm. 2011;1(2):20–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
