Intra-Regional Medical Tourism Demand in Malaysia: A Qualitative Study of Indonesian Medical Tourists' Rationale and Preferences
- PMID: 35528809
- PMCID: PMC9036925
- DOI: 10.21315/mjms2022.29.2.13
Intra-Regional Medical Tourism Demand in Malaysia: A Qualitative Study of Indonesian Medical Tourists' Rationale and Preferences
Abstract
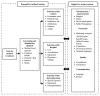
Background: This study aims to explore the Indonesian tourists' demand for medical tourism services in Malaysia. The study also investigates the Indonesian medical tourists' profiles and their preference for Malaysia for medical treatment services.
Methods: This study conducted interviews with 49 potential patients from Indonesia who received cardiac treatment at the National Heart Institute (IJN) in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia.
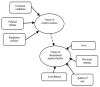
Results: The findings indicate that the key motives of Indonesian tourists travelling to Malaysia for medical treatment are their disappointment with medical practices and inadequate expertise in Indonesia. Besides, they are motivated by peer recommendations, medical expertise, transparency, administration and hospitality in Malaysia. The study findings show that Indonesian medical tourists can be acknowledged as an elite group with stable and above-average income.
Conclusion: Results from the study enable medical tourism marketers to better target and segments their potential medical tourists and develop a strategic medical tourism marketing roadmap. This study shows that the high demand for medical tourism is related to Malaysia's availability of niche medical services. Besides, this paper expands the understanding of medical tourists' decision-making and argues its implications for Malaysian health policy and healthcare delivery for the medical tourism industry sustainability.
Keywords: Indonesia; Malaysia; National Heart Institute; medical tourists; preferences.
© Penerbit Universiti Sains Malaysia, 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None.
Figures
References
-
- Habibi A, Ariffin AAM. Value as a medical tourism driver interacted by experience quality. Anatolia. 2019;30(1):35–46. doi: 10.1080/13032917.2018.1496122. - DOI
-
- Ratnasari RT, Gunawan S, Pitchay AA, Mohd Salleh MC. Sustainable medical tourism: investigating healthcare travel in Indonesia and Malaysia. Int J Healthcar Manag. 2021:1–10. doi: 10.1080/20479700.2020.1870365. - DOI
-
- Seow AN, Choong YO, Moorthy K, Chan LM. Intention to visit Malaysia for medical tourism using the antecedents of theory of planned behaviour: a predictive model. Int J Tour Res. 2017;19(3):383–393. doi: 10.1002/jtr.2120. - DOI
-
- Rahman MK. Medical tourism: tourists’ perceived services and satisfaction lessons from Malaysian hospitals. Tour Rev. 2019;74(3):739–758. doi: 10.1108/TR-01-2018-0006. - DOI
-
- Oktadiana H, Pearce PL. Routledge handbook of tourism cities. Oxon: Routledge; 2020. Tourism in Asean cities: features and directions; pp. 462–476. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources