The polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa attenuate CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats via the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
- PMID: 35528887
- PMCID: PMC9073534
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04679h
The polysaccharides from Grifola frondosa attenuate CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats via the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway
Abstract
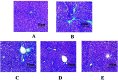
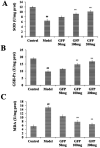
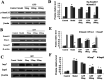
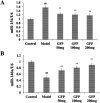
The TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway has been linked to hepatic fibrosis. Previous studies have shown that yellow polysaccharide can prevent the development of hepatic fibrosis. However, it is unclear whether the polysaccharide affects the TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway. In this experiment, 50 experimental rats were randomly divided into a normal control group, model group, low GFP dose group (50 mg kg-1), medium GFP dose group (100 mg kg-1), and high GFP dose group (200 mg kg-1). A cirrhotic portal hypertension rat model was established by a CCl4 compound method. After 12 weeks of intragastric administration, the liver index of the medium dose and high dose group was significantly lower than that of the model group. The hepatic fibrosis lesions of rats in each dose group were improved to different extents, and the effect was most significant in the high dose group. The contents of ALT, AST, TBIL and CIV, PCIII, LN and HA in serum were significantly decreased. The activity of SOD and GSH-Px in the liver tissue of GFP medium and high dose groups was significantly increased and the content of MDA was significantly decreased. The contents of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 were significantly decreased. The western blot results showed that the expressions of p-Smad 2/3, Smad4, PAI-1, Imp7 and Imp8 in medium dose and high dose groups were significantly lower than those in the model group, while the expression of Smad7 was significantly higher than that of the model group. The GFP-treated group was able to reduce the expression level of mi R-154 in liver tissue and increase the expression level of miR-146a. GFP has a significant intervention effect on rat hepatic fibrosis, and its mechanism may inhibit the progression of hepatic fibrosis by inhibiting oxidative stress and inflammatory response and regulating TGF-β1/Smad signaling pathway and mi RNA expression.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hepatoprotective effect of total flavonoids of Mallotus apelta (Lour.) Muell.Arg. leaf against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in rats via modulation of TGF-β1/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 May 23;254:112714. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112714. Epub 2020 Feb 24. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32105750
-
Liuweiwuling tablets attenuate BDL-induced hepatic fibrosis via modulation of TGF-β/Smad and NF-κB signaling pathways.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Jan 10;210:232-241. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.08.029. Epub 2017 Aug 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28864168
-
Ligustroflavone ameliorates CCl4-induced liver fibrosis through down-regulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.Chin J Nat Med. 2021 Mar;19(3):170-180. doi: 10.1016/S1875-5364(21)60018-3. Chin J Nat Med. 2021. PMID: 33781450
-
Transcriptomic analysis reveals pharmacological mechanisms mediating efficacy of Yangyinghuoxue Decoction in CCl4-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 15;15:1364023. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1364023. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38813108 Free PMC article.
-
Ferulic acid attenuates liver fibrosis and hepatic stellate cell activation via inhibition of TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Dec 3;12:4107-4115. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S186726. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 30584275 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
IL-22 alleviates the fibrosis of hepatic stellate cells via the inactivation of NLRP3 inflammasome signaling.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1088. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10522. Epub 2021 Jul 30. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34447480 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Liver Cirrhosis Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 28;22(1):199. doi: 10.3390/ijms22010199. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33379148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Grifola frondosa may play an anti-obesity role by affecting intestinal microbiota to increase the production of short-chain fatty acids.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jan 17;13:1105073. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1105073. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36733799 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical efficacy of total laparoscopic splenectomy for portal hypertension and its influence on hepatic hemodynamics and liver function.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023 Aug 27;15(8):1684-1692. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v15.i8.1684. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2023. PMID: 37701706 Free PMC article.
-
From Cirrhosis to the Dysbiosis (A Loop of Cure or Complications?).Indian J Microbiol. 2024 Sep;64(3):810-820. doi: 10.1007/s12088-024-01267-w. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Indian J Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39282182 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

