Development of cancer immunotherapy based on PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blockade
- PMID: 35528929
- PMCID: PMC9073714
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04590b
Development of cancer immunotherapy based on PD-1/PD-L1 pathway blockade
Abstract
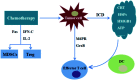
Programmed death receptor 1 (PD-1)/programmed death ligand 1 (PD-L1) blockade therapy has achieved considerable success in various tumours. However, only a fraction of patients benefit from its clinical application, and some patients might be suffer from tumour resistance against PD-1/PD-L1 blockade therapy after the original response. In this review, we summarized the main reasons that caused the low response rate of PD-/PD-L1 blockade therapy: firstly, the off-target of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking agents, which is also the main factor of the side effect of autoimmune disorders; secondly, the insufficient infiltration of T cells in a tumour microenvironment; thirdly, the low immunogenicity of tumor cells; fourth, other immunosuppressive components impairing the therapeutic efficacy of the immunotherapy based on the PD-/PD-L1 blockade, and introducing some updated the delivery system of PD-1/PD-L1 blocking agents and the combination therapy based on PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors and other therapeutics that can complement and promote each other to achieve improved immune response.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
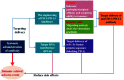
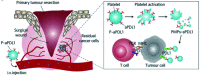
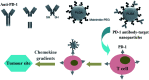
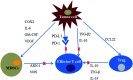
References
-
- Robert C. Long G. V. Brady B. Dutriaux C. Maio M. Mortier L. Hassel J. C. Rutkowski P. McNeil C. Kalinka-Warzocha E. Savage K. J. Hernberg M. M. Lebbé C. Charles J. Mihalcioiu C. Chiarion-Sileni V. Mauch C. Cognetti F. Arance A. Schmidt H. Schadendorf D. Gogas H. Lundgren-Eriksson L. Horak C. Sharkey B. Waxman I. M. Atkinson V. Ascierto P. A. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015;372:311–319. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1411087. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

