Loss of Multiple ABCB Auxin Transporters Recapitulates the Major twisted dwarf 1 Phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 35528937
- PMCID: PMC9069160
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.840260
Loss of Multiple ABCB Auxin Transporters Recapitulates the Major twisted dwarf 1 Phenotypes in Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
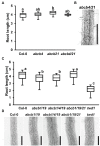
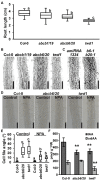
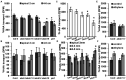
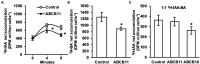
FK506-BINDING PROTEIN 42/TWISTED DWARF 1 (FKBP42/TWD1) directly regulates cellular trafficking and activation of multiple ATP-BINDING CASSETTE (ABC) transporters from the ABCB and ABCC subfamilies. abcb1 abcb19 double mutants exhibit remarkable phenotypic overlap with twd1 including severe dwarfism, stamen elongation defects, and compact circinate leaves; however, twd1 mutants exhibit greater loss of polar auxin transport and additional helical twisting of roots, inflorescences, and siliques. As abcc1 abcc2 mutants do not exhibit any visible phenotypes and TWD1 does not interact with PIN or AUX1/LAX auxin transporters, loss of function of other ABCB auxin transporters is hypothesized to underly the remaining morphological phenotypes. Here, gene expression, mutant analyses, pharmacological inhibitor studies, auxin transport assays, and direct auxin quantitations were used to determine the relative contributions of loss of other reported ABCB auxin transporters (4, 6, 11, 14, 20, and 21) to twd1 phenotypes. From these analyses, the additional reduction in plant height and the twisted inflorescence, root, and silique phenotypes observed in twd1 compared to abcb1 abcb19 result from loss of ABCB6 and ABCB20 function. Additionally, abcb6 abcb20 root twisting exhibited the same sensitivity to the auxin transport inhibitor 1-napthalthalamic acid as twd1 suggesting they are the primary contributors to these auxin-dependent organ twisting phenotypes. The lack of obvious phenotypes in higher order abcb4 and abcb21 mutants suggests that the functional loss of these transporters does not contribute to twd1 root or shoot twisting. Analyses of ABCB11 and ABCB14 function revealed capacity for auxin transport; however, their activities are readily outcompeted by other substrates, suggesting alternate functions in planta, consistent with a spectrum of relative substrate affinities among ABCB transporters. Overall, the results presented here suggest that the ABCB1/19 and ABCB6/20 pairs represent the primary long-distance ABCB auxin transporters in Arabidopsis and account for all reported twd1 morphological phenotypes. Other ABCB transporters appear to participate in highly localized auxin streams or mobilize alternate transport substrates.
Keywords: ABCB transporter; Arabidopsis thaliana; FKBP42/TWD1; auxin; organ twisting.
Copyright © 2022 Jenness, Tayengwa, Bate, Tapken, Zhang, Pang and Murphy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

