A Nomogram-based Model to Predict Neoplastic Risk for Patients with Gallbladder Polyps
- PMID: 35528981
- PMCID: PMC9039700
- DOI: 10.14218/JCTH.2021.00078
A Nomogram-based Model to Predict Neoplastic Risk for Patients with Gallbladder Polyps
Abstract
Background and aims: Gallbladder polyp (GBP) assessment aims to identify the early stages of gallbladder carcinoma. Many studies have analyzed the risk factors for malignant GBPs. In this retrospective study, we aimed to establish a more accurate predictive model for potential neoplastic polyps in patients with GBPs.
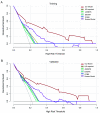
Methods: We developed a nomogram-based model in a training cohort of 233 GBP patients. Clinical information, ultrasonographic findings, and blood test findings were analyzed. Mann-Whitney U test and multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to identify independent predictors and establish the nomogram model. An internal validation was conducted in 225 consecutive patients. Performance and clinical benefit of the model were evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curves and decision curve analysis (DCA), respectively.
Results: Age, cholelithiasis, carcinoembryonic antigen, polyp size, and sessile shape were confirmed as independent predictors of GBP neoplastic potential in the training group. Compared with five other proposed prediction methods, the established nomogram model presented better discrimination of neoplastic GBPs in the training cohort (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.846) and the validation cohort (AUC: 0.835). DCA demonstrated that the greatest clinical benefit was provided by the nomogram compared with the other five methods.
Conclusions: Our developed preoperative nomogram model can successfully be used to evaluate the neoplastic potential of GBPs based on simple clinical variables that maybe useful for clinical decision-making.
Keywords: Gallbladder polyps; Neoplastic polyp; Nomogram model; Preoperative diagnosis.
© 2022 Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interests related to this publication.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A nomogram-based model and ultrasonic radiomic features for gallbladder polyp classification.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 Jul;37(7):1380-1388. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15841. Epub 2022 Apr 21. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022. PMID: 35357026
-
Development and Validation of a Preoperative Prediction Model for Neoplastic Gallbladder Polyps.Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2025 Feb 25;86(2):1-15. doi: 10.12968/hmed.2024.0800. Br J Hosp Med (Lond). 2025. PMID: 39998148
-
Predictive factors of neoplastic gallbladder polyps: Outcomes of 278 patients.Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017 May;28(3):202-206. doi: 10.5152/tjg.2017.16698. Epub 2017 Mar 17. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2017. PMID: 28316322
-
Development and validation of a preoperative nomogram for predicting gallbladder adenoma.Surg Endosc. 2025 Mar;39(3):1749-1760. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11480-9. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39808305
-
Is cholecystectomy a reasonable treatment option for simple gallbladder polyps larger than 10 mm?World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Apr 14;21(14):4248-54. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i14.4248. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25892875 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
A Nomogram-Based Model for Predicting the Risk of Severe Acute Cholangitis Occurrence.Int J Gen Med. 2023 Jul 25;16:3139-3150. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S416108. eCollection 2023. Int J Gen Med. 2023. PMID: 37521070 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of Pathogenic Bacteria Distribution and Related Factors in Recurrent Acute Cholangitis.Infect Drug Resist. 2023 Jul 20;16:4729-4740. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S418752. eCollection 2023. Infect Drug Resist. 2023. PMID: 37492797 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Neoplastic Polyp in Patients With Gallbladder Polyps Using Interpretable Machine Learning Models: Retrospective Cohort Study.Cancer Med. 2025 Mar;14(5):e70739. doi: 10.1002/cam4.70739. Cancer Med. 2025. PMID: 40052528 Free PMC article.
-
Diacerein ameliorates acetaminophen hepatotoxicity in rats via inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-κB and upregulating PPAR-γ signal.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Jul;49(7):5863-5874. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07366-5. Epub 2022 Apr 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35366176 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram for predicting mortality risk within 30 days in sepsis patients admitted in the emergency department: A retrospective analysis.PLoS One. 2024 Jan 25;19(1):e0296456. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296456. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38271366 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patel K, Dajani K, Iype S, Chatzizacharias NA, Vickramarajah S, Singh P, et al. Incidental non-benign gallbladder histopathology after cholecystectomy in an United Kingdom population: Need for routine histological analysis? World J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;8(10):685–692. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v8.i10.685. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
