Updated Perspectives on Keratinocytes and Psoriasis: Keratinocytes are More Than Innocent Bystanders
- PMID: 35529056
- PMCID: PMC9075909
- DOI: 10.2147/PTT.S327310
Updated Perspectives on Keratinocytes and Psoriasis: Keratinocytes are More Than Innocent Bystanders
Abstract
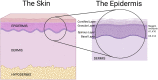
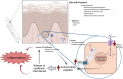
Psoriasis is a complex disease triggered by genetic, immunologic, and environmental stimuli. Many genes have been linked to psoriasis, like the psoriasis susceptibility genes, some of which are critical in keratinocyte biology and epidermal barrier function. Still, the exact pathogenesis of psoriasis is unknown. In the disease, the balance between the proliferative and differentiative processes of keratinocytes becomes altered. Multiple studies have highlighted the role of dysregulated immune cells in provoking the inflammatory responses seen in psoriasis. In addition to immune cells, accumulating evidence shows that keratinocytes are involved in psoriasis pathogenesis, as discussed in this review. Although certain immune cell-derived factors stimulate keratinocyte hyperproliferation, activated keratinocytes can also produce anti-microbial peptides, cytokines, and chemokines that can promote their proliferation, as well as recruit immune cells to help initiate and reinforce inflammatory feedback loops. Psoriatic keratinocytes also show intrinsic differences from normal keratinocytes even after removal from the in vivo inflammatory environment; thus, psoriatic keratinocytes have been found to exhibit abnormal calcium metabolism and possible epigenetic changes that contribute to psoriasis. The Koebner phenomenon, in which injury promotes the development of psoriatic lesions, also provides evidence for keratinocytes' contributions to disease pathogenesis. Furthermore, transgenic mouse studies have confirmed the importance of keratinocytes in the etiology of psoriasis. Finally, in addition to immune cells and keratinocytes, data in the literature support roles for other cell types, tissues, and systems in psoriasis development. These other contributors are all potential targets for therapies, suggesting the importance of a holistic approach when treating psoriasis.
Keywords: Koebner phenomenon; anti-microbial peptides; inflammation; innate immunity; skin.
© 2022 Ortiz-Lopez et al.
Conflict of interest statement
LIO-L and VC report no conflicts of interest in this work. WBB is an inventor of an Augusta University patent (8,808,715) for the use of phosphatidylglycerol to modulate keratinocyte function.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sprouty1 exerts a preventive effect on the initiation of psoriasis by inhibiting innate immune antimicrobial peptide cathelicidin and immunocytes.Cell Prolif. 2022 Oct;55(10):e13290. doi: 10.1111/cpr.13290. Epub 2022 Jun 18. Cell Prolif. 2022. PMID: 35716036 Free PMC article.
-
Epidermal activation of the small GTPase Rac1 in psoriasis pathogenesis.Small GTPases. 2019 May;10(3):163-168. doi: 10.1080/21541248.2016.1273861. Epub 2017 May 4. Small GTPases. 2019. PMID: 28055293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Type1 Interferons Potential Initiating Factors Linking Skin Wounds With Psoriasis Pathogenesis.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 25;10:1440. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01440. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31293591 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Daphnetin inhibits proliferation and inflammatory response in human HaCaT keratinocytes and ameliorates imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin lesion in mice.Biol Res. 2020 Oct 20;53(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40659-020-00316-0. Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 33081840 Free PMC article.
-
PI3Kδ Sustains Keratinocyte Hyperproliferation and Epithelial Inflammation: Implications for a Topically Druggable Target in Psoriasis.Cells. 2021 Oct 2;10(10):2636. doi: 10.3390/cells10102636. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34685616 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evidence-based modalities in the management of Psoriasis and Psoriatic arthritis.Bioinformation. 2023 Jun 30;19(6):679-684. doi: 10.6026/97320630019679. eCollection 2023. Bioinformation. 2023. PMID: 37885781 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effects of topical ramelteon on imiquimod-induced psoriasiform inflammation in mice.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Aug;397(8):6231-6248. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03017-7. Epub 2024 Mar 6. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38446218
-
Tapinarof Nanogels as a Promising Therapeutic Approach.Pharmaceutics. 2025 Jun 1;17(6):731. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics17060731. Pharmaceutics. 2025. PMID: 40574044 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Effect of Lecigel, Cetiol®CC, Activonol-6, Activonol-M, 1,3-Propanediol, Soline, and Fucocert® (LCAA-PSF) Treatment on Imiquimod-Induced Psoriasis-like Skin in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 14;25(14):7720. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147720. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39062965 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of soluble skin surface protein levels for monitoring psoriasis vulgaris in adult psoriasis patients using non-invasive transdermal analysis patch: A pilot study.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Mar 2;10:1072160. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1072160. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 36936209 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

