Effect of PCSK9 Inhibitor on Blood Lipid Levels in Patients with High and Very-High CVD Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35529059
- PMCID: PMC9072011
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/8729003
Effect of PCSK9 Inhibitor on Blood Lipid Levels in Patients with High and Very-High CVD Risk: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Objectives: We aimed to investigate the effects of proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (PCSK9) inhibitor on blood lipid levels in patients with high and very-high cardiovascular risk.
Design: 14 trials (n = 52,586 patients) comparing treatment with or without PCSK9 inhibitors were retrieved from PubMed and Embase updated to 1st Jun 2021. The data quality of included studies was assessed by two independent researchers using the Cochrane systematic review method. All-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, and changes in serum low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), apolipoprotein B (ApoB), lipoprotein (a) (LP (a)), non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and apolipoprotein A1 (ApoA1) from baseline were analyzed using Rev Man 5.1.0 software.
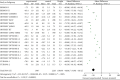
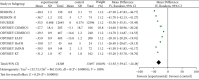
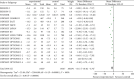
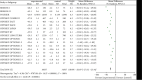
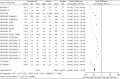
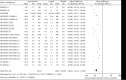
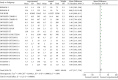
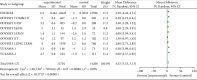
Results: Compared with treatments without PCSK9 inhibitor, addition of PCSK9 inhibitors (evolocumab and alirocumab) had obvious decreasing effects on the levels of LDL-C [MD = -46.86, 95% CI (-54.99 to -38.72), P < 0.00001], TC [MD = -31.92, 95% CI (-39.47 to -24.38), P < 0.00001], TG [MD = -8.13, 95% CI (-10.48 to -5.79), P < 0.00001], LP(a) [MD = -26.69, 95% CI (-27.93 to -25.44), P < 0.00001], non-HDL-C [MD = -42.86, 95% CI (-45.81 to -39.92), P < 0.00001], and ApoB [MD = -38.44, 95% CI (-42.23 to -34.65), P < 0.00001] in high CVD risk patients. Conversely, changes of HDL-C [MD = 6.27, CI (5.17 to 7.36), P < 0.00001] and ApoA1 [MD = 4.33, 95% CI (3.53 to 5.13), P < 0.00001] from baseline were significantly more in high cardiovascular disease risk patients who received PCSK9 inhibitors treatment.
Conclusion: Addition of PCSK9 inhibitors to standard therapy resulted in definite improvement in blood lipid levels compared with therapies that did not include them.
Copyright © 2022 Yue Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Grundy S. M., Feingold K. R. South Dartmouth, MA, USA: In: Endotext, MDText.com, Inc.; 2000. Guidelines for the management of high blood cholesterol.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
