An integrated metabolomics and 16S rRNA gene sequencing approach exploring the molecular pathways and potential targets behind the effects of Radix Scrophulariae
- PMID: 35529111
- PMCID: PMC9073378
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra03912k
An integrated metabolomics and 16S rRNA gene sequencing approach exploring the molecular pathways and potential targets behind the effects of Radix Scrophulariae
Abstract
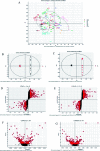
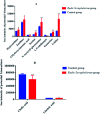
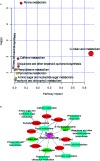
To assess the impact of the caecal microbiota on faecal metabolic phenotypes in the presence of Radix Scrophulariae (Chinese name: Xuanshen), an integrated approach involving 16S rRNA gene sequencing combined with ultrahigh-performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry (UHPLC/TOF-MS)-based faecal metabolomics was applied to Radix Scrophulariae-treated rats. Interestingly, Radix Scrophulariae led to significant gut microbiota changes at the phylum and genus levels in treated rats compared to control rats. Additionally, distinct changes in faecal metabolites, including linoleic acid (LA), guanosine, inosine, hypoxanthine, xanthine, 4-hydroxycinnamic acid, cholic acid, N-acetyl-d-glucosamine, l-urobilinogen and uridine, were observed in Radix Scrophulariae-treated rats. Of these, seven metabolites were up-regulated, and the remaining three metabolites were down-regulated. Moreover, there were substantial associations between altered levels of gut microbiota genera and discrepant levels of faecal metabolites, particularly for compounds involved in LA and purine metabolism. These results demonstrated that the gut microbiota is altered in association with faecal metabolism following treatment with Radix Scrophulariae. Our findings suggest that further application of this 16S rRNA gene sequencing and UHPLC/TOF-MS-based metabolomics approach will facilitate the assessment of the pharmacological action of Radix Scrophulariae and thus expand the scope of this herb.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Radix Scrophulariae on Hyperthyroidism Assessed by Metabonomics and Network Pharmacology.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Sep 28;12:727735. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.727735. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34650432 Free PMC article.
-
Variations in gut microbiota and fecal metabolic phenotype associated with depression by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and LC/MS-based metabolomics.J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017 May 10;138:231-239. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2017.02.008. Epub 2017 Feb 10. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2017. PMID: 28219800
-
To elucidate the mechanism of "Scrophulariae Radix-Fritillaria" in goiter by integrated metabolomics and serum pharmaco-chemistry.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 17;15:1206718. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1206718. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38828449 Free PMC article.
-
High throughput metabolomics-proteomics investigation on metabolic phenotype changes in rats caused by Radix Scrophulariae using ultra-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry.RSC Adv. 2019 Jun 6;9(31):17791-17800. doi: 10.1039/c8ra10443c. eCollection 2019 Jun 4. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35520561 Free PMC article.
-
[Chemical constituents, pharmacological activities, processing and clinical application of traditional Chinese medicine Scrophulariae Radix: a review].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023 Aug;48(16):4302-4319. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20230123.201. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 37802857 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Herbal medicines in Alzheimer's disease and the involvement of gut microbiota.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 16;15:1416502. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1416502. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39081953 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Radix Scrophulariae Extracts Exert Effect on Hyperthyroidism via MST1/Hippo Signaling Pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2023 Nov;29(11):998-1006. doi: 10.1007/s11655-023-3744-7. Epub 2023 Sep 4. Chin J Integr Med. 2023. PMID: 37661231
References
-
- Wei-Liang G. Chang-Xun C. Qi W. et al., Effects of Chinese herb medicine Radix Scrophulariae on ventricular remodeling. Pharmazie. 2010;65:770–775. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

