Activating peroxymonosulfate by halogenated and methylated quinones: performance and mechanism
- PMID: 35529206
- PMCID: PMC9070648
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra04789a
Activating peroxymonosulfate by halogenated and methylated quinones: performance and mechanism
Abstract
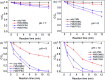
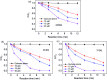
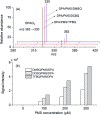
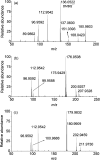
Activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by halogenated and methylated quinones for destroying sulfamethoxazole (SMX) was investigated, where 2,6-dimethyl-1,4-benzoquinone (DMBQ), 2,6-dichloro-1,4-benzoquinone (DCBQ), and tetrafluoro-1,4-benzoquinone (TFBQ) were chosen as model quinones. The PMS could be activated by halogenated and methylated quinones efficiently for SMX degradation, and the process showed high pH and quinones dependency. Different from PMS activated by ultraviolet (UV), singlet oxygen (1O2) instead of hydroxyl radical (˙OH) and sulfate radical (SO4˙-) was the primary oxidizing species in the activation process. The formation of 1O2 was confirmed by various quenching studies combined with chemical probes (9,10-diphenylanthracene (DPA)). By sampling in situ and monitoring in real time, droplet spray ionization mass spectrometry (DSI-MS) was applied to capture and identify the intermediates generated in the activation process. A possible mechanism for PMS activation was proposed accordingly. It was found that a series of reactions between PMS and halogenated/methylated quinones formed a dioxirane intermediate, and the subsequent decomposition of this intermediate produced the 1O2. These findings would help to better understand the interactions between PMS and quinones, and provide a novel activator for PMS activation toward environmental contaminants.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Activation of Peroxymonosulfate by Benzoquinone: A Novel Nonradical Oxidation Process.Environ Sci Technol. 2015 Nov 3;49(21):12941-50. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.5b03595. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Environ Sci Technol. 2015. PMID: 26452059
-
Electrochemical activation of peroxymonosulfate (PMS) by carbon cloth anode for sulfamethoxazole degradation.Chemosphere. 2022 Jan;287(Pt 2):132094. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132094. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34492410
-
Molecular mechanism of metal-independent decomposition of lipid hydroperoxide 13-HPODE by halogenated quinoid carcinogens.Free Radic Biol Med. 2013 Oct;63:459-66. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.05.008. Epub 2013 May 14. Free Radic Biol Med. 2013. PMID: 23680403 Free PMC article.
-
Facile synthesis of oxygen vacancies enriched α-Fe2O3 for peroxymonosulfate activation: A non-radical process for sulfamethoxazole degradation.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Oct 5;419:126447. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126447. Epub 2021 Jun 20. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 34182419
-
Evolution of Singlet Oxygen by Activating Peroxydisulfate and Peroxymonosulfate: A Review.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 24;18(7):3344. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18073344. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33804931 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Efficiency and Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship of Monoaromatics Oxidation by Quinone-Activated Persulfate.Front Chem. 2021 Sep 1;9:580643. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.580643. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 34540795 Free PMC article.
-
Selective degradation of acetaminophen from hydrolyzed urine by peroxymonosulfate alone: performances and mechanisms.RSC Adv. 2021 Dec 16;11(63):40022-40032. doi: 10.1039/d1ra07891g. eCollection 2021 Dec 13. RSC Adv. 2021. PMID: 35494137 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duan X. G. Sun H. Q. Shao Z. P. Wang S. B. Appl. Catal., B. 2018;224:973–982. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.11.051. - DOI
-
- Xing Z. P. Zhang J. Q. Cui J. Y. Yin J. W. Zhao T. Y. Kuang J. Y. Xiu Z. Y. Wan N. Zhou W. Appl. Catal., B. 2018;225:452–467. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2017.12.005. - DOI
-
- Chen P. Wang F. L. Chen Z. F. Zhang Q. X. Su Y. H. Shen L. Z. Yao K. Liu Y. Cai Z. W. Lv W. Y. Liu G. G. Appl. Catal., B. 2017;204:250–259. doi: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.11.040. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

