Polyacrylamide crosslinked by bis-vinylimidazolium bromide for high elastic and stable hydrogels
- PMID: 35529219
- PMCID: PMC9070750
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra05201a
Polyacrylamide crosslinked by bis-vinylimidazolium bromide for high elastic and stable hydrogels
Abstract
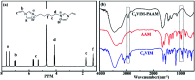
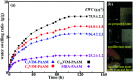
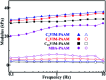
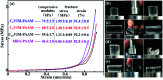
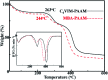
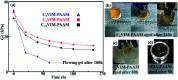
A series of ionic compounds 1,n-dialkyl-3,3'-bis-l-vinylimidazolium bromide (C n VIM) are prepared and employed to crosslink acrylamide for polyacrylamide (PAAM) hydrogel preparation via in situ solution polymerization. The swelling behavior, mechanical properties and thermal stability of the prepared C n VIM crosslinked PAAM hydrogels are investigated. C n VIM effectively crosslink the PAAM networks to form porous structures in the hydrogel, which could stably absorb water as much as 75.9 fold in weight without structural degradation. The prepared hydrogels could endure compressive stress up to 1.95 MPa and compressive deformation more than 90%. Meanwhile, the C n VIM crosslinked networks show superior thermal stability, and could retain the structural integrity under 150 °C for more than 240 h. The swelling degradation resistance, mechanical strength and thermal stability of C n VIM crosslinked hydrogels are much better than those of a conventional N,N'-methylenebisacrylamide crosslinked PAAM hydrogel. Using bis-vinylimidazolium bromides as crosslinkers provides an optional strategy for constructing thermally and mechanically robust hydrogel networks.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A high temperature-resistant, strong, and self-healing double-network hydrogel for profile control in oil recovery.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025 Feb;679(Pt B):490-502. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2024.10.077. Epub 2024 Oct 19. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2025. PMID: 39490267
-
Anisotropic swelling and mechanical behavior of composite bacterial cellulose-poly(acrylamide or acrylamide-sodium acrylate) hydrogels.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010 Jan;3(1):102-11. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Jun 23. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2010. PMID: 19878907
-
A strong, tough, and osteoconductive hydroxyapatite mineralized polyacrylamide/dextran hydrogel for bone tissue regeneration.Acta Biomater. 2019 Apr 1;88:503-513. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.02.019. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Acta Biomater. 2019. PMID: 30772515
-
Hydrolytic Stability of Crosslinked, Highly Alkaline Diallyldimethylammonium Hydroxide Hydrogels.Gels. 2022 Oct 19;8(10):669. doi: 10.3390/gels8100669. Gels. 2022. PMID: 36286170 Free PMC article.
-
Multiarm Star-Crosslinked Hydrogel: Polymer Network with Thermoresponsive Free-End Chains Densely Connected to Crosslinking Points.Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021 Apr;42(8):e2000558. doi: 10.1002/marc.202000558. Epub 2020 Nov 26. Macromol Rapid Commun. 2021. PMID: 33244811
Cited by
-
Microstructured thermo-responsive double network granular hydrogels.Mater Adv. 2025 Jun 16;6(15):5089-5099. doi: 10.1039/d5ma00511f. eCollection 2025 Jul 28. Mater Adv. 2025. PMID: 40575680 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

