Functional photoacoustic microscopy of hemodynamics: a review
- PMID: 35529339
- PMCID: PMC9046529
- DOI: 10.1007/s13534-022-00220-4
Functional photoacoustic microscopy of hemodynamics: a review
Abstract
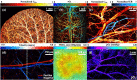
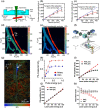
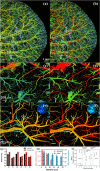
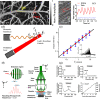
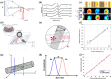
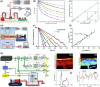
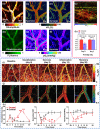
Functional blood imaging can reflect tissue metabolism and organ viability, which is important for life science and biomedical studies. However, conventional imaging modalities either cannot provide sufficient contrast or cannot support simultaneous multi-functional imaging for hemodynamics. Photoacoustic imaging, as a hybrid imaging modality, can provide sufficient optical contrast and high spatial resolution, making it a powerful tool for in vivo vascular imaging. By using the optical-acoustic confocal alignment, photoacoustic imaging can even provide subcellular insight, referred as optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy (OR-PAM). Based on a multi-wavelength laser source and developed the calculation methods, OR-PAM can provide multi-functional hemodynamic microscopic imaging of the total hemoglobin concentration (CHb), oxygen saturation (sO2), blood flow (BF), partial oxygen pressure (pO2), oxygen extraction fraction, and metabolic rate of oxygen (MRO2). This concise review aims to systematically introduce the principles and methods to acquire various functional parameters for hemodynamics by photoacoustic microscopy in recent studies, with characteristics and advantages comparison, typical biomedical applications introduction, and future outlook discussion.
Keywords: Calculation methods; Hemodynamics; Multi-functional imaging; Photoacoustic imaging.
© Korean Society of Medical and Biological Engineering 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
