Pharmacology of Kappa Opioid Receptors: Novel Assays and Ligands
- PMID: 35529436
- PMCID: PMC9068900
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.873082
Pharmacology of Kappa Opioid Receptors: Novel Assays and Ligands
Abstract
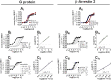
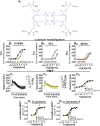
The present study investigated the in vitro pharmacology of the human kappa opioid receptor using multiple assays, including calcium mobilization in cells expressing chimeric G proteins, the dynamic mass redistribution (DMR) label-free assay, and a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) assay that allows measurement of receptor interaction with G protein and β-arrestin 2. In all assays, dynorphin A, U-69,593, and [D-Pro10]dyn(1-11)-NH2 behaved as full agonists with the following rank order of potency [D-Pro10]dyn(1-11)-NH2 > dynorphin A ≥ U-69,593. [Dmt1,Tic2]dyn(1-11)-NH2 behaved as a moderate potency pure antagonist in the kappa-β-arrestin 2 interaction assay and as low efficacy partial agonist in the other assays. Norbinaltorphimine acted as a highly potent and pure antagonist in all assays except kappa-G protein interaction, where it displayed efficacy as an inverse agonist. The pharmacological actions of novel kappa ligands, namely the dynorphin A tetrameric derivative PWT2-Dyn A and the palmitoylated derivative Dyn A-palmitic, were also investigated. PWT2-Dyn A and Dyn A-palmitic mimicked dynorphin A effects in all assays showing similar maximal effects but 3-10 fold lower potency. In conclusion, in the present study, multiple in vitro assays for the kappa receptor have been set up and pharmacologically validated. In addition, PWT2-Dyn A and Dyn A-palmitic were characterized as potent full agonists; these compounds are worthy of further investigation in vivo for those conditions in which the activation of the kappa opioid receptor elicits beneficial effects e.g. pain and pruritus.
Keywords: BRET; G protein-coupled receptor; PWT2-dyn A; biased agonism; calcium mobilization; dyn A-palmitic; kappa opioid receptor; label-free.
Copyright © 2022 Sturaro, Malfacini, Argentieri, Djeujo, Marzola, Albanese, Ruzza, Guerrini, Calo’ and Molinari.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
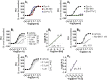



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

