Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A2 Is Constitutively Expressed in Cartilage and Upregulated in Inflamed Synovium From hTNF-Alpha Transgenic Mice
- PMID: 35529439
- PMCID: PMC9067626
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.835697
Orphan Nuclear Receptor NR4A2 Is Constitutively Expressed in Cartilage and Upregulated in Inflamed Synovium From hTNF-Alpha Transgenic Mice
Abstract
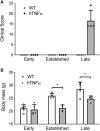
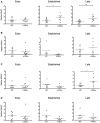
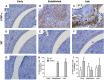
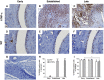
Orphan nuclear receptor 4A2 (NR4A2/Nurr1) is a constitutively active transcription factor with potential roles in the onset and progression of inflammatory arthropathies. NR4A2 is overexpressed in synovium and cartilage from individuals with rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriatic arthritis, and osteoarthritis. This study documents the expression and tissue localization of NR4A2 and upstream regulator nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) in the human tumor necrosis factor-alpha (hTNF-α) transgenic mouse model of RA. Since TNF-α is a potent inducer of NR4A2 in vitro, we hypothesized that NR4A2 would also be upregulated and active during disease progression in this model. Expression levels of NR4A2, related receptors NR4A1 (Nur77) and 3 (NOR1), and NF-κB1 transcripts were quantified by RT-qPCR in hTNF-α and wild-type joints at three stages of disease. The protein distribution of NR4A2 and NF-κB subunit RelA (p65) was analyzed by quantitative immunohistochemistry. Global gene expression of 88 RA-related genes was also screened and compared between groups. Consistent with previous reports on the hTNF-α model, transgenic mice exhibited significant weight loss and severely swollen paws by 19 weeks of age compared to age-matched wild-type controls. NR4A1-3 and NF-κB1 were constitutively expressed at disease onset and in healthy joints. NF-κB1 transcript levels increased 2-fold in hTNF-α paws with established disease (12 weeks), followed by a 2-fold increase in NR4A2 at the late disease stage (19 weeks). NR4A2 and RelA proteins were overexpressed in inflamed synovium prior to symptoms of arthritis, suggesting that gene expression changes documented in whole paws were largely driven by elevated expression in diseased synovium. Broader screening of RA-related genes by RT-qPCR identified several differentially expressed genes in hTNF-α joints including those encoding inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, matrix-degrading enzymes and inhibitors, cell surface receptors, intracellular signaling proteins and transcription factors. Consensus binding sites for NR4A receptors and NF-κB1 were enriched in the promoters of differentially expressed genes suggesting central roles for these transcription factors in this model. This study is the first comprehensive analysis of NR4A2 in an animal model of RA and validates the hTNF-α model for testing of small molecules and genetic strategies targeting this transcription factor.
Keywords: NFkB (RelA); NR4A2 gene; TNF-α; cartilage; inflammation; nuclear receptors; rheumatoid arthritis; synovium.
Copyright © 2022 Lilley, Alarcon, Ngo, Araujo, Marrero and Mix.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Compensatory Expression of Nur77 and Nurr1 Regulates NF-κB-Dependent Inflammatory Signaling in Astrocytes.Mol Pharmacol. 2018 Oct;94(4):1174-1186. doi: 10.1124/mol.118.112631. Epub 2018 Aug 15. Mol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30111648 Free PMC article.
-
Orphan nuclear receptor NR4A2 induces transcription of the immunomodulatory peptide hormone prolactin.J Inflamm (Lond). 2015 Feb 18;12:13. doi: 10.1186/s12950-015-0059-2. eCollection 2015. J Inflamm (Lond). 2015. PMID: 25717285 Free PMC article.
-
Induction of NR4A orphan nuclear receptor expression in macrophages in response to inflammatory stimuli.J Biol Chem. 2005 Aug 12;280(32):29256-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M502606200. Epub 2005 Jun 17. J Biol Chem. 2005. PMID: 15964844
-
Inflammation: a role for NR4A orphan nuclear receptors?Biochem Soc Trans. 2011 Apr;39(2):688-93. doi: 10.1042/BST0390688. Biochem Soc Trans. 2011. PMID: 21428963 Review.
-
The Paradoxical Roles of Orphan Nuclear Receptor 4A (NR4A) in Cancer.Mol Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;19(2):180-191. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-20-0707. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Mol Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33106376 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Natural products and synthetic analogs as selective orphan nuclear receptor 4A (NR4A) modulators.Histol Histopathol. 2024 May;39(5):543-556. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-689. Epub 2023 Dec 13. Histol Histopathol. 2024. PMID: 38116863 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NR4A1-3 nuclear receptor activity and immune cell dysregulation in rheumatic diseases.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 22;9:874182. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.874182. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35935773 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Afzali M. F., Popichak K. A., Burton L. H., Klochak A. L., Wilson W. J., Safe S., et al. (2018). A Novel Diindolylmethane Analog, 1,1-Bis(3'-Indolyl)-1-(p-Chlorophenyl) Methane, Inhibits the Tumor Necrosis Factor-Induced Inflammatory Response in Primary Murine Synovial Fibroblasts through a Nurr1-dependent Mechanism. Mol. Immunol. 101, 46–54. 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Binder N. B., Puchner A., Niederreiter B., Hayer S., Leiss H., Blüml S., et al. (2013). Tumor Necrosis Factor-Inhibiting Therapy Preferentially Targets Bone Destruction but Not Synovial Inflammation in a Tumor Necrosis Factor-Driven Model of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 65, 608–617. 10.1002/art.37797 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bonta P. I., van Tiel C. M., Vos M., Pols T. W., van Thienen J. V., Ferreira V., et al. (2006). Nuclear Receptors Nur77, Nurr1, and NOR-1 Expressed in Atherosclerotic Lesion Macrophages Reduce Lipid Loading and Inflammatory Responses. Arterioscler Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 26 (10), 2288–2294. 10.1161/01.ATV.0000238346.84458.5d - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

