Medicinal Cannabis and Central Nervous System Disorders
- PMID: 35529444
- PMCID: PMC9070567
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.881810
Medicinal Cannabis and Central Nervous System Disorders
Abstract
Cannabinoids, including those found in cannabis, have shown promise as potential therapeutics for numerous health issues, including pathological pain and diseases that produce an impact on neurological processing and function. Thus, cannabis use for medicinal purposes has become accepted by a growing majority. However, clinical trials yielding satisfactory endpoints and unequivocal proof that medicinal cannabis should be considered a frontline therapeutic for most examined central nervous system indications remains largely elusive. Although cannabis contains over 100 + compounds, most preclinical and clinical research with well-controlled dosing and delivery methods utilize the various formulations of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), the two most abundant compounds in cannabis. These controlled dosing and delivery methods are in stark contrast to most clinical studies using whole plant cannabis products, as few clinical studies using whole plant cannabis profile the exact composition, including percentages of all compounds present within the studied product. This review will examine both preclinical and clinical evidence that supports or refutes the therapeutic utility of medicinal cannabis for the treatment of pathological pain, neurodegeneration, substance use disorders, as well as anxiety-related disorders. We will predominately focus on purified THC and CBD, as well as other compounds isolated from cannabis for the aforementioned reasons but will also include discussion over those studies where whole plant cannabis has been used. In this review we also consider the current challenges associated with the advancement of medicinal cannabis and its derived potential therapeutics into clinical applications.
Keywords: addiction; anxiety; cannabinoid 1 receptor; cannabinoid 2 receptor; clinical research; neurodegeneration; pain; serotonin 1a receptor.
Copyright © 2022 Ortiz, McMahon and Wilkerson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
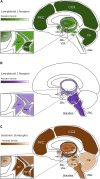
Figures
References
-
- Abraham A. D., Leung E. J. Y., Wong B. A., Rivera Z. M. G., Kruse L. C., Clark J. J., et al. (2020). Orally Consumed Cannabinoids Provide Long-Lasting Relief of Allodynia in a Mouse Model of Chronic Neuropathic Pain. Neuropsychopharmacology 45 (7), 1105–1114. 10.1038/s41386-019-0585-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agurell S., Carlsson S., Lindgren J. E., Ohlsson A., Gillespie H., Hollister L. (1981). Interactions of delta 1-tetrahydrocannabinol with Cannabinol and Cannabidiol Following Oral Administration in Man. Assay of Cannabinol and Cannabidiol by Mass Fragmentography. Experientia 37 (10), 1090–1092. 10.1007/BF02085029 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

