Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
- PMID: 35529473
- PMCID: PMC9019427
- DOI: 10.1515/med-2022-0463
Zoledronate promotes ECM degradation and apoptosis via Wnt/β-catenin
Abstract
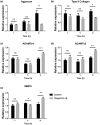
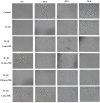
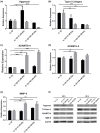
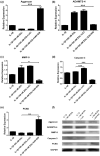
This study examined the potential mechanism of zoledronate on interleukin (IL)-1β-induced temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis (TMJOA) chondrocytes, using IL-1β-induced rabbit immortalized mandibular condylar chondrocytes cultured with zoledronate. Cell viability, apoptosis, mRNA, and protein expression of relevant genes involved in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, apoptosis, and Wnt/β-catenin signaling were examined. The involvement of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling was examined using Wnt/β-catenin inhibitor (2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-7,8-dihydro-5H-thiopyrano[4,3-d]pyrimidin-4-ol (XAV-939)) and activator lithium chloride (LiCl). Aggrecan and type II collagen were downregulated by zoledronate, especially with 100 nM for 48 h (p < 0.01), consistently with the upregulation of A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs-4 (ADAMTS-4) (p < 0.001), matrix metalloprotease-9 (MMP-9) (p < 0.01), caspase-3 (p < 0.001) and downregulation of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) (p < 0.01). The apoptotic rate increased from 34.1% to 45.7% with 100 nM zoledronate for 48 h (p < 0.01). The effects of zoledronate on ADAMTs4 (p < 0.001), MMP-9 (p < 0.001), caspase-3 (p < 0.001), and PCNA (p < 0.01) were reversed by XAV-939, while LiCl increased caspase-3 expression (p < 0.01). In conclusion, zoledronate enhances IL-1β-induced ECM degradation and cell apoptosis in TMJOA chondrocytes. Wnt/β-catenin signaling might be involved in this process, but additional studies are necessary to determine the exact involvement of Wnt/β-catenin signaling in chondrocytes after zoledronate treatment.
Keywords: Wnt signaling pathway; apoptosis; extracellular matrix; osteoarthritis; temporomandibular joint; zoledronate.
© 2022 Jialing Xiao et al., published by De Gruyter.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors of this work have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Jiawei Yanghe decoction ameliorates cartilage degradation in vitro and vivo via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Biomed Pharmacother. 2020 Feb;122:109708. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109708. Epub 2019 Dec 30. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020. PMID: 31918279
-
Role of Wnt-5A in interleukin-1beta-induced matrix metalloproteinase expression in rabbit temporomandibular joint condylar chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2009 Sep;60(9):2714-22. doi: 10.1002/art.24779. Arthritis Rheum. 2009. PMID: 19714632
-
Chondroprotective effects of palmatine on osteoarthritis in vivo and in vitro: A possible mechanism of inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin and Hedgehog signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 May;34:129-138. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.02.029. Epub 2016 Mar 2. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26945831
-
Mechanical stress reduces secreted frizzled-related protein expression and promotes temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis via Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Bone. 2022 Aug;161:116445. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2022.116445. Epub 2022 May 16. Bone. 2022. PMID: 35589066
-
Licochalcone A Inhibits MMPs and ADAMTSs via the NF-κB and Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathways in Rat Chondrocytes.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;43(3):937-944. doi: 10.1159/000481645. Epub 2017 Sep 29. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 28957807
Cited by
-
Synergistic effects of sequential treatment with doxorubicin and zoledronic acid on anticancer effects in estrogen receptor-negative breast cancer cells.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jun;398(6):7475-7488. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03737-w. Epub 2025 Jan 4. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39754678
References
-
- Zarb GA, Carlsson GE. Temporomandibular disorders: osteoarthritis. J Orofac Pain. 1999;13(4):295–306. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
